

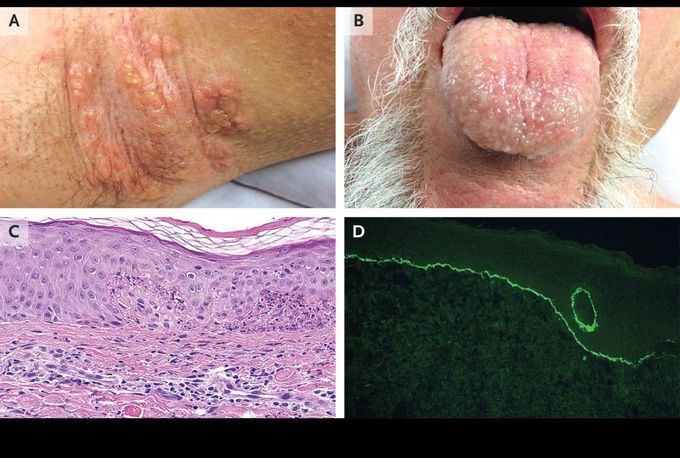
Vancomycin-Induced Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis
A 67-year-old man presented to the emergency department with a 1-day history of a diffuse rash. He had a history of prostate cancer treated with radiation therapy, which was complicated by the development of a urethral stricture, for which he had undergone surgery. He had recently received a diagnosis of polymicrobial pubic osteomyelitis and myositis from a urethral fistula, for which treatment with cefepime and vancomycin was started. Ten days after the initiation of antibiotic therapy, he noticed a burning sensation on his tongue, which was followed by the rapid development of erythematous patches with blistering involving his abdomen, arms, and legs. Physical examination showed vesicles in the axilla (Panel A) and on the tongue (Panel B) and erythematous plaques with vesicles on his abdomen, arms, and legs. He had no fevers, eosinophilia, or organ dysfunction. Histopathological examination of a biopsy specimen showed neutrophilic papillitis with microvesicles (Panel C, hematoxylin and eosin). Direct immunofluorescence revealed linear deposition of IgA along the basement membrane zone (Panel D). Vancomycin-induced linear IgA bullous dermatosis was suspected, and vancomycin was discontinued (while cefepime was continued). No further lesions developed 1 day after the withdrawal of vancomycin, and complete resolution of the mucocutaneous lesions was noted at 1 month of follow-up.
Preparation for USMLEScope of practice of NREMTSuturing

