

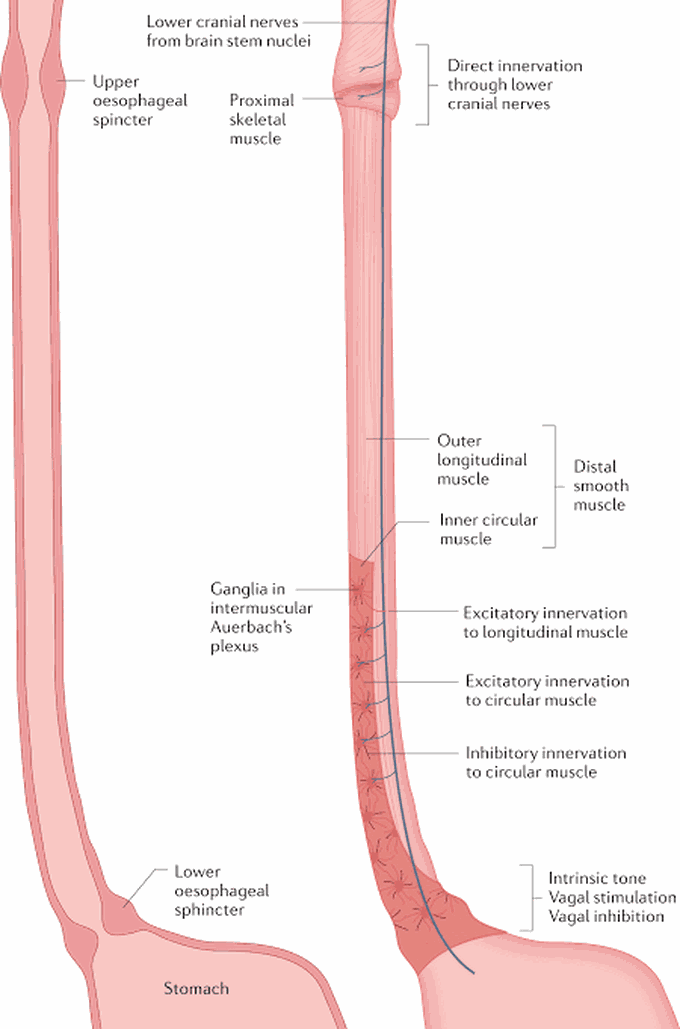
Achalasia diagnosis
Achalasia can be overlooked or misdiagnosed because it has symptoms similar to other digestive disorders. To test for achalasia, your doctor is likely to recommend: Esophageal manometry. This test measures the rhythmic muscle contractions in your esophagus when you swallow, the coordination and force exerted by the esophagus muscles, and how well your lower esophageal sphincter relaxes or opens during a swallow. This test is the most helpful when determining which type of motility problem you might have. X-rays of your upper digestive system (esophagram). X-rays are taken after you drink a chalky liquid that coats and fills the inside lining of your digestive tract. The coating allows your doctor to see a silhouette of your esophagus, stomach and upper intestine. You may also be asked to swallow a barium pill that can help to show a blockage of the esophagus. Upper endoscopy. Your doctor inserts a thin, flexible tube equipped with a light and camera (endoscope) down your throat, to examine the inside of your esophagus and stomach. Endoscopy can be used to define a partial blockage of the esophagus if your symptoms or results of a barium study indicate that possibility. Endoscopy can also be used to collect a sample of tissue (biopsy) to be tested for complications of reflux such as Barrett's esophagus.

