

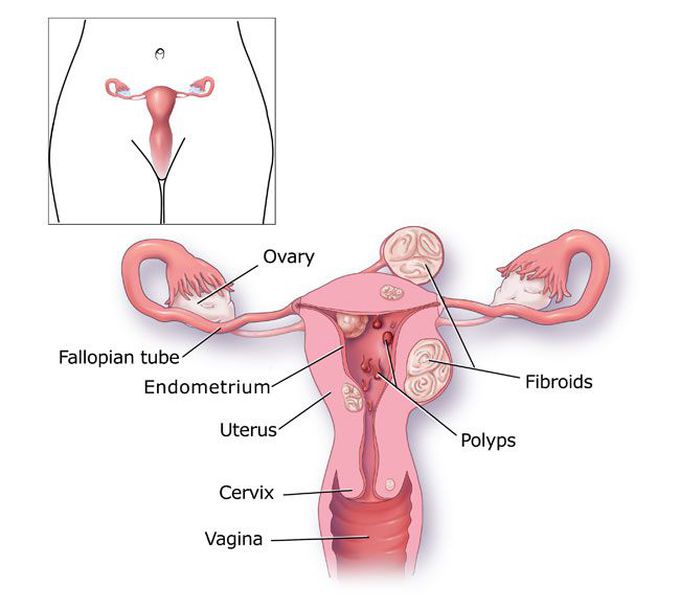
Complications of menorrhagia
Excessive or prolonged menstrual bleeding can lead to other medical conditions, including: Anemia. Menorrhagia can cause blood loss anemia by reducing the number of circulating red blood cells. The number of circulating red blood cells is measured by hemoglobin, a protein that enables red blood cells to carry oxygen to tissues. Iron deficiency anemia occurs as your body attempts to make up for the lost red blood cells by using your iron stores to make more hemoglobin, which can then carry oxygen on red blood cells. Menorrhagia may decrease iron levels enough to increase the risk of iron deficiency anemia. Signs and symptoms include pale skin, weakness and fatigue. Although diet plays a role in iron deficiency anemia, the problem is complicated by heavy menstrual periods. Severe pain. Along with heavy menstrual bleeding, you might have painful menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea). Sometimes the cramps associated with menorrhagia are severe enough to require medical evaluation.

