

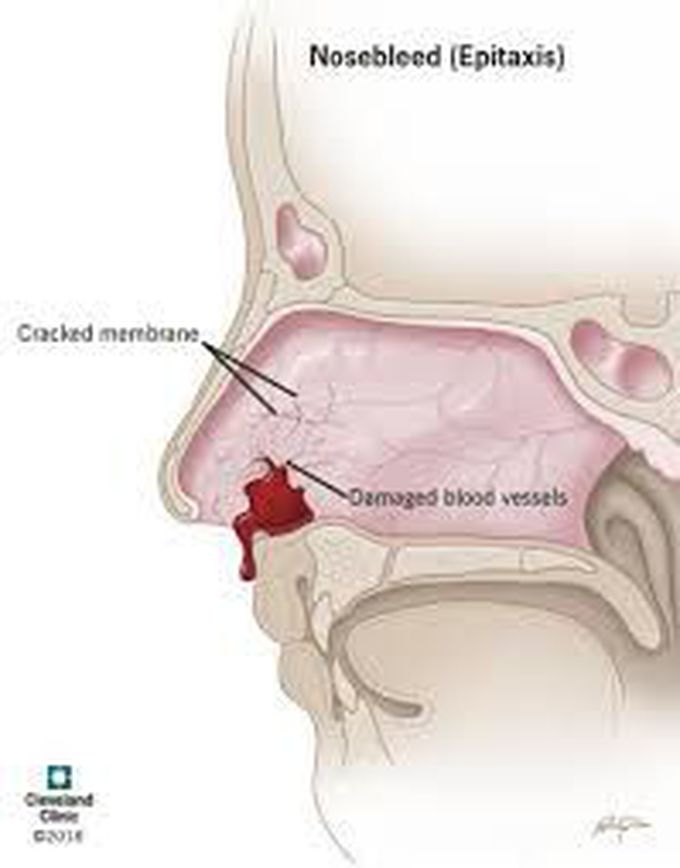
Treatment for epistaxis
Treatments depend on the cause and could include: Nasal packing. Gauze, special nasal sponges or foam or an inflatable latex balloon is inserted into your nose to create pressure at the site of the bleed. The material is often left in place for 24 to 48 hours before being removed by a healthcare professional. Cauterization. This procedure involves applying a chemical substance (silver nitrate) or heat energy (electrocautery) to seal the bleeding blood vessel. A local anesthetic is sprayed in the nostril first to numb the inside of your nose. Medication adjustments/new prescriptions. Reducing or stopping the amount of blood thinning medications can be helpful. In addition, medications for controlling blood pressure may be necessary. Tranexamic (Lystedaâ), a medication to help blood clot, may be prescribed. Foreign body removal if this is the cause of the nose bleed. Surgical repair of a broken nose or correction of a deviated septum if this is the cause of the nosebleed. Ligation. In this procedure, the culprit blood vessel is tied off to stop the bleeding.

