

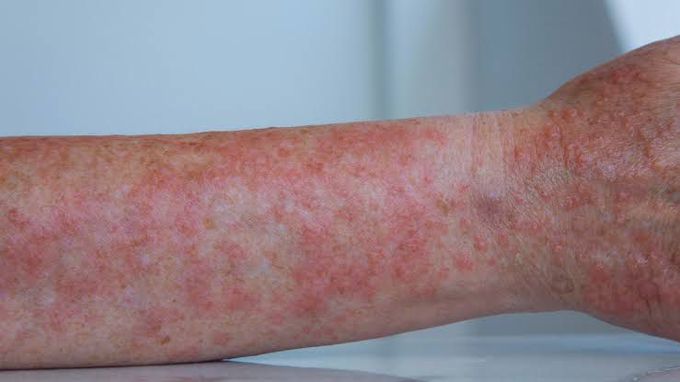
Causes of polymorphous light eruption
The exact cause of polymorphous light eruption isn't understood. The rash appears in people who have developed sensitivity to sunlight, especially ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or other sources, such as tanning beds. This is called photosensitivity. It leads to immune system activity that causes a rash. UV radiation UV radiation is a wavelength of sunlight in a range too short for the human eye to see. UV light that reaches the earth is divided into two wavelength bands — ultraviolet A (UVA) and ultraviolet B (UVB). A person with photosensitivity can react to both types of UV radiation. UVB doesn't penetrate glass. UVA does. Exposure to sunlight through windows or even sunscreen-protected skin may cause a reaction in some people with photosensitivity. Photosensitivity With polymorphous light eruption, sensitivity to sunlight lessens with repeated exposure. Features of polymorphous light eruption are somewhat predictable: An episode is most likely to occur after the first one or two times of sun exposure after a long period of no exposure, such as in spring or early summer. Episodes are less likely to happen as the summer progresses. After the first episode, it's likely to happen each year. Some people gradually become less sensitive over several years and eventually no longer experience the yearly rash.

