

Intracranial Hemorrhage
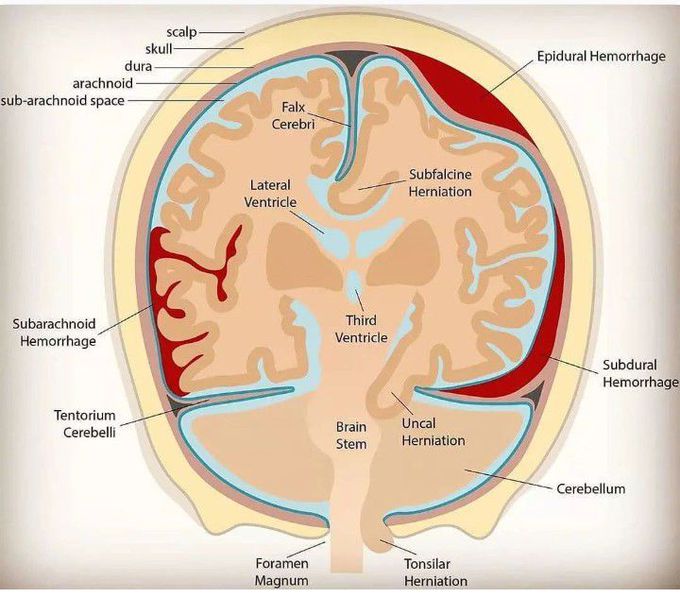
What is an intracranial hemorrhage? Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) refers to acute bleeding inside your skull or brain. It’s a life-threatening emergency. What are the types of ICH? There are four main types of ICH: epidural hematoma. subdural hematoma. subarachnoid hemorrhage. intracerebral hemorrhage. A hematoma is a collection of blood, in a clot or ball, outside of a blood vessel. 1) Epidural hematoma: Its happen when blood accumulates between your skull and the outermost covering of your brain.It typically follows a head injury, and usually with a skull fracture. High-pressure bleeding is a prominent feature. If you have an epidural hematoma, you may briefly lose consciousness and then regain consciousness. 2) Subdural hematoma: Is a collection of blood on the surface of your brain. It’s typically the result of your head moving rapidly forward and stopping, such as in a car accident. However, it could also suggest abuse in children. This is the same type of movement a child experiences when being shaken. It's more common than other ICHs in older people and people with history of heavy alcohol use. 3) Subarachnoid hemorrhage: Is when there’s bleeding between the brain and the thin tissues that cover the brain. These tissues are called meninges. The most common cause is trauma, but it can also be caused by rupture of a major blood vessel in the brain, such as from an intracerebral aneurysm.A sudden, sharp headache usually comes before a subarachnoid hemorrhage. Typical symptoms also include loss of consciousness and vomiting. 4) Intracerebral hemorrhage: Is when there’s bleeding inside of your brain. This is the most common type of ICH that occurs with a stroke. It’s not usually the result of injury.

