

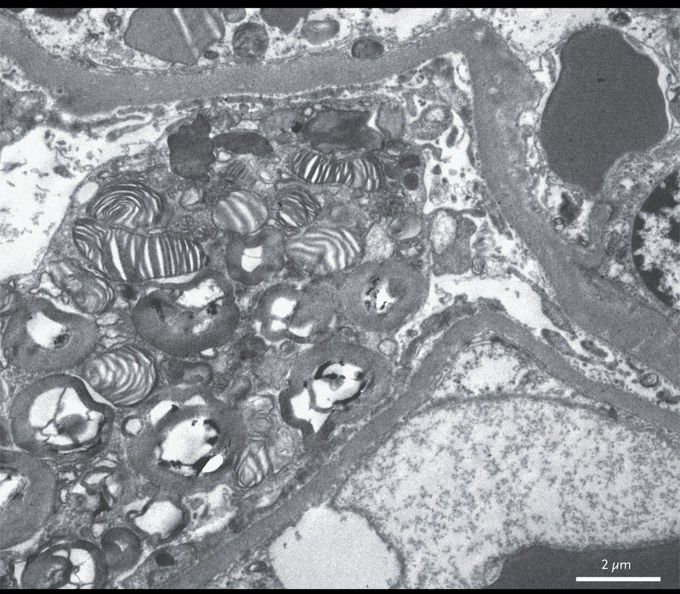
Zebra Bodies in the Kidney
A 21-year-old man with a 10-year history of intermittent burning pain in his arms and legs presented to the nephrology clinic after noticing foamy urine for 1 month. The physical examination, which included a neurologic evaluation, was unremarkable, but urinalysis revealed proteinuria. The serum creatinine level was 81 μmol per liter (0.9 mg per deciliter) (reference range, 62 to 106 μmol per liter [0.7 to 1.2 mg per deciliter]), and the urinary protein excretion was 1335 mg per 24 hours (reference range, 0 to 140). Biopsy of the kidney showed the presence of vacuoles within podocytes. Electron microscopy revealed layered membrane structures appearing as so-called zebra bodies within enlarged lysosomes in the podocytes. A diagnosis of Fabry’s disease was confirmed when a mutation in the gene encoding alpha-galactosidase A (GLA) was detected. Fabry’s disease is an X-linked lysosomal storage disorder caused by mutations that result in low or absent activity of the enzyme alpha-galactosidase A. This deficiency results in the accumulation of globotriaosylceramide in cells, resulting in the formation of the characteristic zebra bodies. Treatment of Fabry’s disease includes enzyme-replacement therapy; however, this treatment was not available where the patient was living. Carbamazepine was initiated for pain management. At the 10-month follow-up, he continued to have proteinuria but had a normal creatinine level, and his pain was well controlled.

