

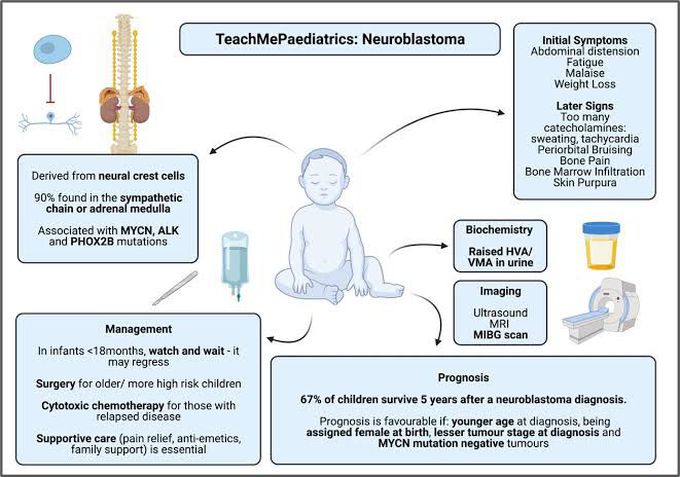
Diagnosis of neuroblastoma
A variety of tests and investigations will be needed to diagnose neuroblastoma. These include a biopsy of the tumour, blood and bone marrow tests, X-rays, CT or MRI scans, and a special nuclear medicine scan called an MIBG scan. These tests are carried out to confirm the diagnosis of neuroblastoma, and to find the exact position of the original site of neuroblastoma within the body and to see whether it has spread. This process is known as staging. A specific type of urine test will also be done. Nearly all children with neuroblastoma (9 out of 10) will have substances called vanillylmandelic acid (VMA), or homovanillic acid (HVA), in their urine. Measuring the VMA and HVA in the urine can help to confirm the diagnosis. Your child will also have their VMA and HVA levels checked during and after treatment. The levels of these substances will fall if the treatment is working. As these chemicals are produced by the tumour cells, and can be used to measure tumour activity, they are sometimes known as tumour markers. Most children will have an MIBG (meta-iodo-benzyl guanidine) scan. MIBG is a substance that’s taken up by neuroblastoma cells. It’s given by injection into the blood stream. Attaching a small amount of radioactive iodine to the MIBG enables any neuroblastoma tissue to be seen by a radiation scanner. Sometimes MIBG can be used as a treatment.

