

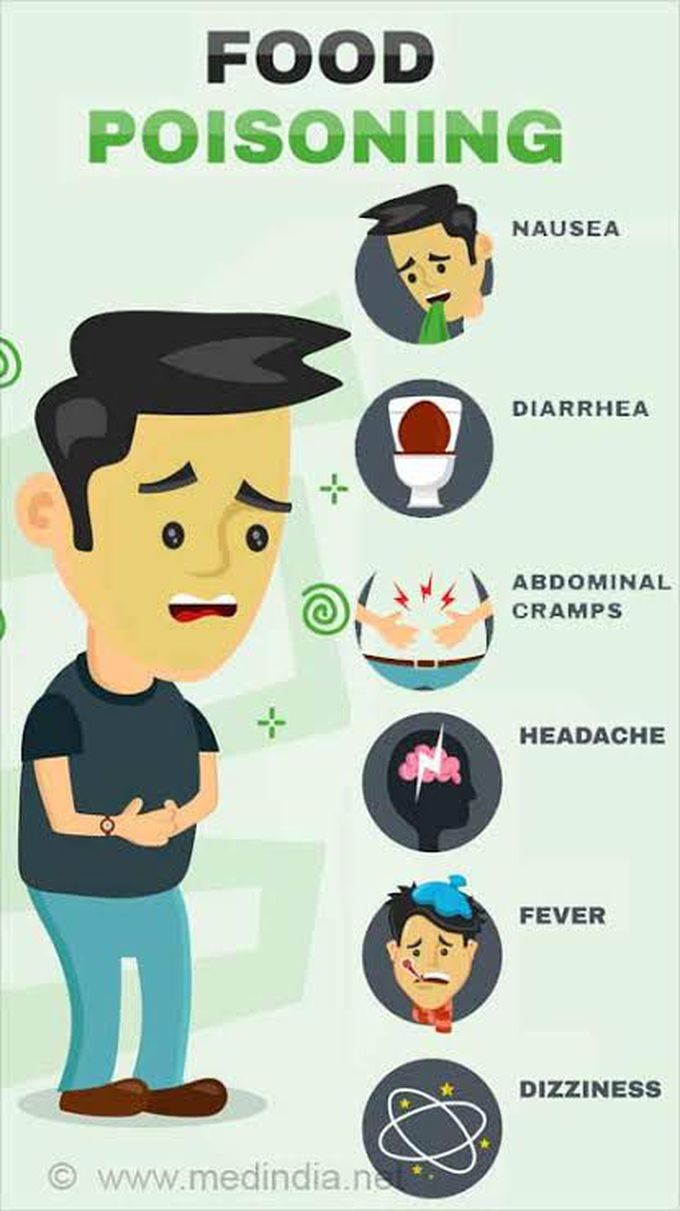
Causes of food poisoning
Food can become contaminated at any stage during its production, processing or cooking. For example, it can become contaminated by: not cooking food thoroughly (particularly meat) not correctly storing food that needs to be chilled at below 5C keeping cooked food unrefrigerated for a long period eating food that has been touched by someone who is ill or has been in contact with someone with diarrhoea and vomiting cross-contamination (where harmful bacteria are spread between food, surfaces and equipment) Cross-contamination can occur, for example, if you prepare raw chicken on a chopping board and don't wash the board before preparing food that won't be cooked (such as salad), as the harmful bacteria can be spread from the chopping board to the salad. It can also occur if raw meat is stored above ready-to-eat meals and juices from the meat drip on to the food below.

