

Phases of wound healing
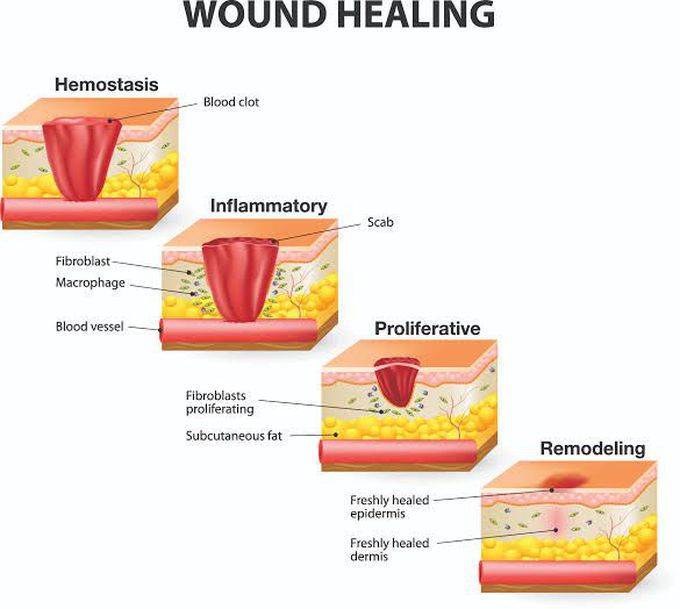
Stages of wound healing All wounds go through different healing processes, ranging from the initial wound reaction to the later stages of creating new skin. Simple wounds, such as those without extensive tissue damage or infection, take about 4–6 weeks to heal. This does not include scar tissue, however, which takes longer to form and heal. Scar tissue will never return to 100% strength, but it will reach about 80% strength around 11–14 weeks after sustaining the initial wound. The following sections describe the wound healing process in more detail. Hemostasis phase The hemostasis phase occurs as the injury happens and is the first response from the body. The wound causes blood and other fluids to leave the body. The body responds by trying to stop this flow of blood. Affected blood vessels constrict to reduce blood flow. As some researchTrusted Source notes, platelets and thrombocytes in the blood start to clump together near the open wound, forming a fibrin network. This thickens the blood in the immediate area to help stop the bleeding. This newly formed clot also prevents germs from getting into the body. This restores the skin’s function as a barrier against dirt and other potentially infectious agents so that healing can begin. The platelets release chemicals that alert the surrounding cells to start the next process and heal the wound. Inflammatory phase During the inflammatory phase, the cleaning and healing of the area begin. There is generally some inflammation in the area, as the immune cells rush to the damaged tissue. White blood cells enter the area to start cleaning out the wound and move any waste away from the site and out of the body. Proliferative phase The proliferative phase of wound healing occurs when the wound is stable. The body’s focus during this stage is to close the wound, create new tissue, and repair any damaged blood vessels in the area. This occurs over the course of four different processes: Epithelialization: This is the process of creating new skin tissue in the various layers of damaged skin. Angiogenesis: This is the creation of new blood vessels in the area of the wound healing. Collagen formation: This is the building up of strength in the tissue of the wound. Contraction: This is the reduction and eventual closing of the wound size and area. The combined connective tissue and blood vessels is called granulation tissue. This granulation tissue starts to form around 4 daysTrusted Source into a wound’s healing process. Remodeling phase During the remodeling phase, the internal wound is mostly healed. The process switches to creating strong skin to replace the temporary tissue in the area. Some research notes that this process occurs around 2 or 3 weeksTrusted Source after the injury and can last for 1 year or longer. This is the active scar tissue phase of healing. The body replaces the temporary granular tissue from the early wound with stronger scar tissue. As time goes on, the scar tissue has an increased concentration of collagen, which makes it stronger.

