
Sadiaover 2 years ago
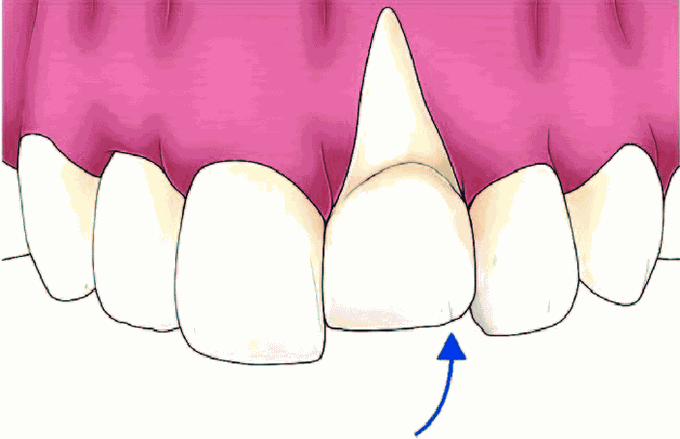
Intrusive Luxation
Intrusive luxation has been defined as dislocation of a tooth in an axial direction into the alveolar bone. This dislocation is considered complete when the tooth is enveloped by surrounding tissues or partial when the incisal border of the crown is visible (Andreasen, 1984).
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!
