

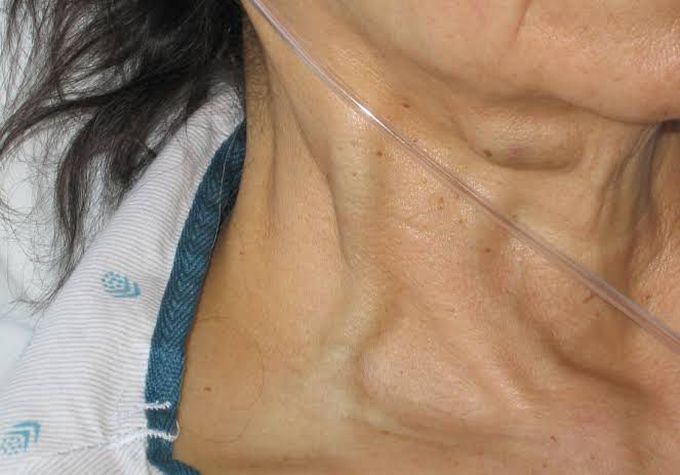
Causes of Jugular vein distension
Many cardiovascular conditions can cause an increase in your CVP and lead to JVD. Some of these conditions include: Right sided heart failure: This occurs when the right side of your heart cannot pump blood effectively, causing the jugular vein to bulge from fluid accumulation. Pulmonary hypertension: High blood pressure in the arteries between the lungs and the heart can cause the jugular vein to bulge. Constrictive pericarditis: This condition occurs when the pericardium, which is the sac around the heart, becomes infected or inflamed and scarred. When this happens, the heart’s ability to fill with blood is restricted, leading to an accumulation of blood in the veins. Superior vena cava obstruction: This is a rare condition wherein the superior vena cava becomes partially or fully blocked. It is usually due to a blood clot or tumor. Tricuspid valve stenosis: This condition occurs when the opening of the tricuspid valve, which regulates blood flow in the heart, becomes narrowed. As a result, blood cannot flow effectively. Cardiac tamponade: This is a serious condition that occurs when fluid accumulates in the pericardium. This buildup compresses the heart and restricts blood flow.

