

Iqraalmost 4 years ago
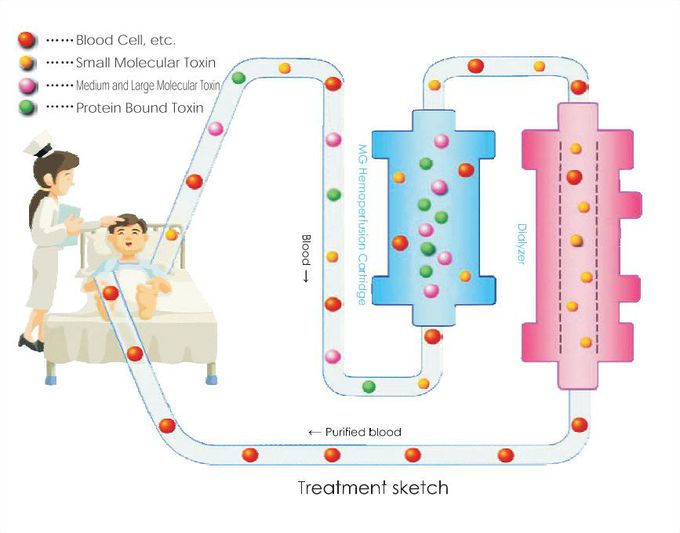
Hemoperfusion
Hemoperfusion refers to the circulation of anticoagulated blood through an extracorporeal circuit with a disposable, adsorbent-containing cartridge (typically activated charcoal or an exchange resin). Two types of hemoperfusion are commonly used: Charcoal hemoperfusion, which has been used to treat liver (hepatic) failure, various types of poisoning, and certain autoimmune diseases when coated with antigens or antibodies.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

