

Nurse.ali fadel abassalmost 4 years ago
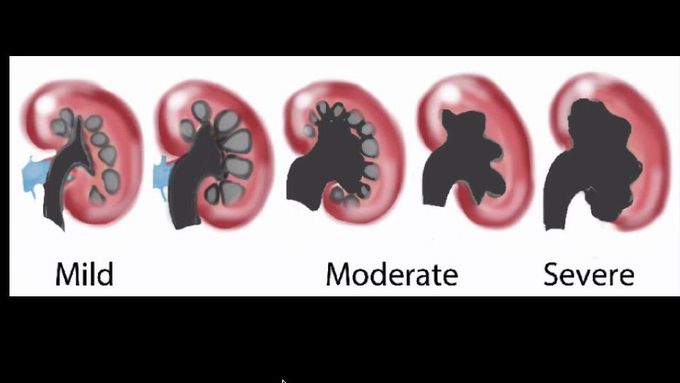
Sepsis is a systemic inflammatory response to infection that can lead to multi-organ dysfunction, failure, and even death. Urosepsis is sepsis caused by infections of the urinary tract, including cystitis, or lower urinary tract and bladder infections, and pyelonephritis, or upper urinary tract and kidney infections. Nearly 25 percent of sepsis cases originate from the urogenital tract. This activity reviews the etiology, pathophysiology, and presentation of urosepsis and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in the management of patients with this condition.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

