

Maria Rosa Ferreiraalmost 2 years ago
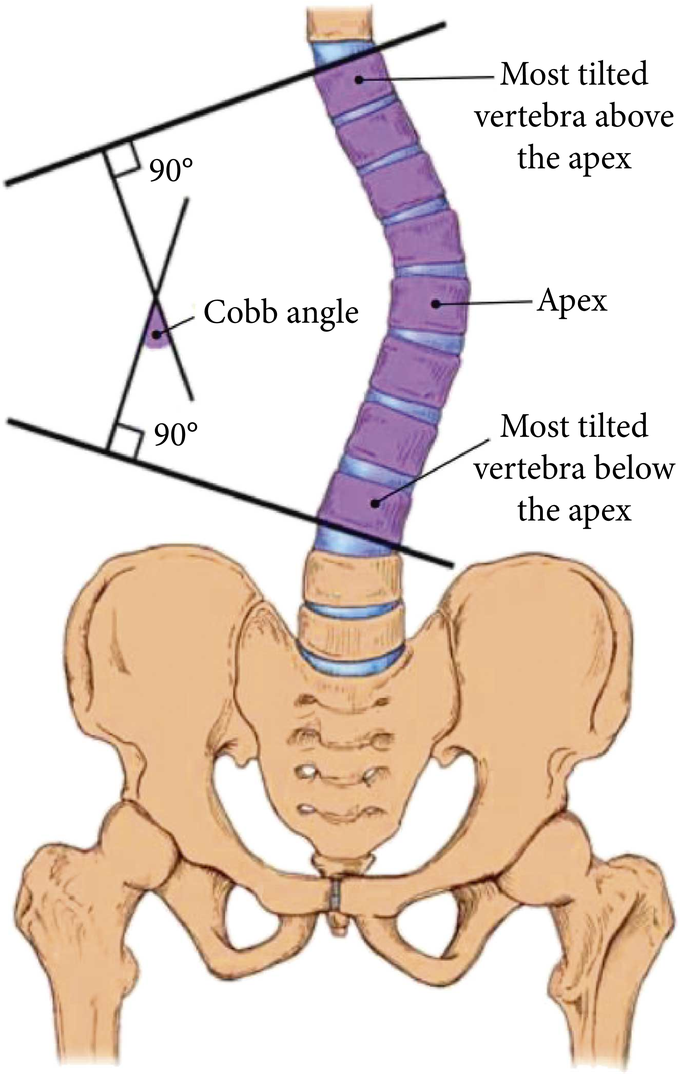
Cobb Angle Measurement
The most common quantification of scoliosis is the Cobb angle. The measurement of Cobb angle involves estimating the angle between the two tangents of the upper and lower endplates of the upper and lower end vertebra, respectively, as shown in the figure. The severity definition for scoliosis is determined using the Cobb angle. The condition of a spine is associated with the spinal curve instead of scoliosis when the Cobb angle is less than 10 degrees. A Cobb angle in the range of 10 to 20 degrees is considered as mild scoliosis. Scoliosis severity is moderate when the Cobb angle ranges from 20 to 40 degrees. A Cobb angle greater than 40 degrees denotes severe scoliosis. Source: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/cmmm/2019/6357171/
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

