

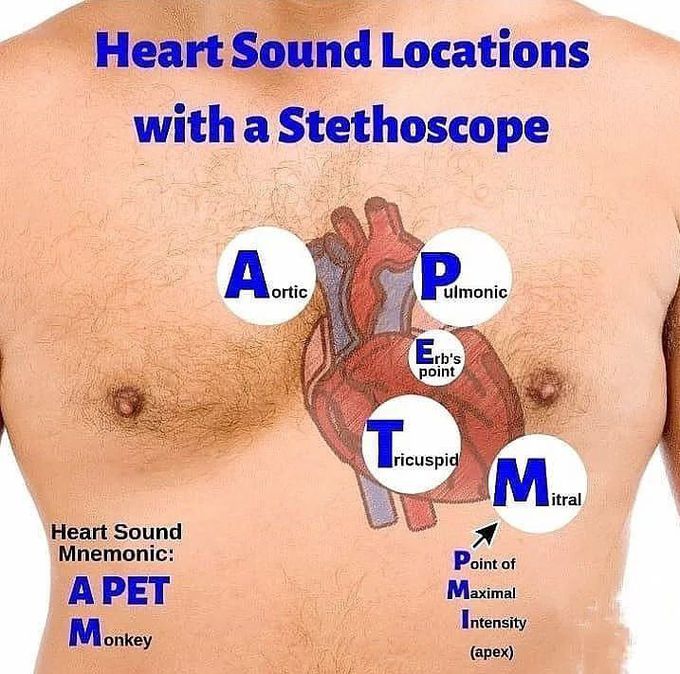
Heart sound locations with stethoscope
The 5 points of auscultation of the heart include the aortic, pulmonic, tricuspid, and mitral valve as well as an area called Erb’s point, where S2 is best heard. The five points of auscultation of the heart center around the heart valves and allow the listener to hear detailed mechanics of each heart valve. To listen to the aortic area, the stethoscope is placed on the right side of the sternum (i.e., the breastbone located in middle of the chest) at the 2nd intercostal space (i.e., the space between the first and second ribs). The pulmonic area is located on the left side of the sternum at the 2nd intercostal space and Erb’s point is located on the left side at the 3rd intercostal space (i.e., the space between the second and third ribs). To listen to the tricuspid area, the stethoscope is placed on the lower left sternal border at the 4th intercostal space (i.e., the space between the third and fourth ribs). Lastly, to listen to the mitral area of the heart, the stethoscope is placed at the apex of the heart, or the area on the left side of the sternum at the 5th intercostal space (i.e. the space between the fourth and five ribs) on the midclavicular line.

