

Abeer Fatimaalmost 2 years ago
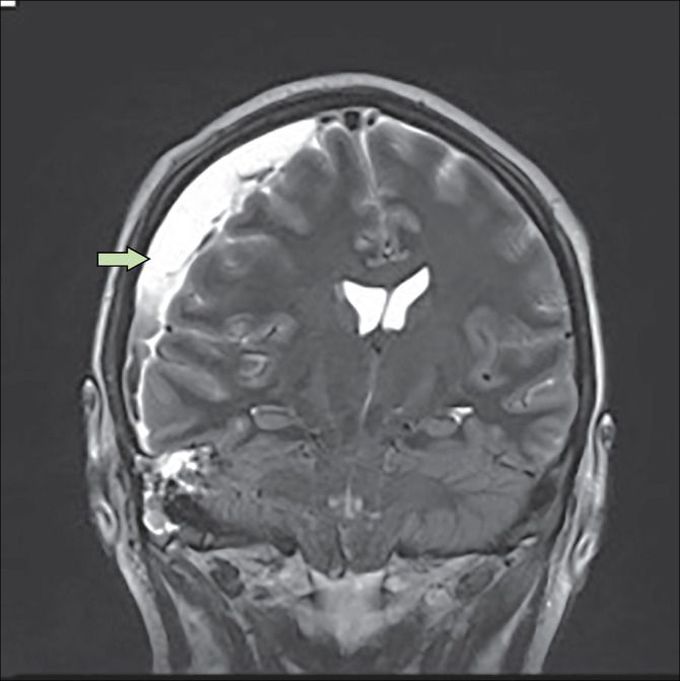
Subdural Empyema
Subdural empyema refers to collection of pus between dura and arachnoid mater. It is an intracranial abscess. The consequences includes focal neurological deficits secondary to extrinsic pressure and inflammation of brain and meninges. The patient with subdural empyema typically gives history of prior airway infection, otitis media, or sinusitis. Seizures, high grade fever, confusion, vomiting, and amblyopia are common complaints. Management includes stabilization of patient, antibiotics, and surgical drainage. Reference: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1168415-treatment#d6 Image via: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(18)30096-3/fulltext
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!
Related posts
Symptoms of HyperekplexiaOdontogenic infectionsOral candidiasisDandy Walker Malformation | Diagnosis symptoms and treatment2-Minute Neuroscience: Brain AneurysmsSeizures (Epilepsy) Nursing NCLEX: Tonic-Clonic, Generalized, Focal, SymptomsStroke: Causes, Risk Factors, Treatment, and Prevention | Mass General BrighamNeurofibromatosisAbsence seizuresSymptoms of absence seizures

