
No more polio!!
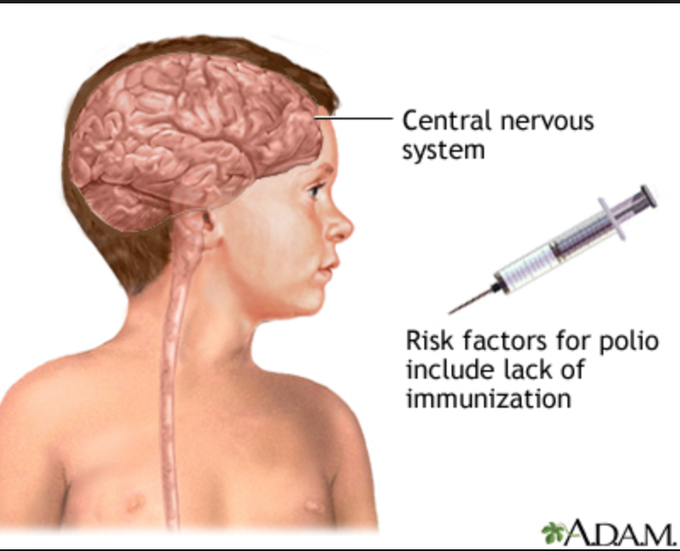
Poliomyelitis (Polio)- Viral disease caused by polio virus. This disease causes inflammation of the spinal cord resulting in nerve damage that leads to lifelong paralysis. This virus spreads through contaminated food and water as well as through coughing and sneezing. Humans are the only natural host of the polio virus. The polio virus mainly affects children less than 5 years old especially in the disadvantaged areas. To prevent polio, inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV) was invented in 1951 by American researcher and virologist, Dr. Jonas Salk, and live attenuated vaccine was invented in 1961 by another Polish American Researcher, Dr. Albert Sabin. After that, polio was nearly eliminated worldwide. The last polio case seen in the United States of America was in 1979. Risk factors: 1. Children less than 5 years old. 2. Born in endemic circulation countries like Afghanistan, Pakistan or Nigeria. 3. Less availability of polio vaccine. Cause: When polio virus enters into the body it goes to the mucosal cells of oropharynx and small intestine and replicates to make more virus by the RNA polymerase. The virus lyses the mucosal cell then travels to the nearby lymph node and then enters into the blood circulation. From the blood it goes to the muscle and invades motor neuron. Then it travels retrograde to anterior horn of spinal cord and leads to inflammation, followed by damage of spinal cord. The neuron dies and the muscle of the limbs do not get signals from the brain. Symptoms: 1. High fever 2. Intense muscle pain (from spasm and weakness) 3. Loss of muscle reflexes 4. Asymmetric paralysis in legs 5. Difficulty of breathing (from damaged motor nerve of the diaphragm) Diagnosis: 1. Recovered polio virus from stool or throat swab 2. Lumber puncture - CSF examination: increased WBC and poliovirus RNA Complication: 1. Respiratory muscle involvement leads to respiratory failure and death (from damaged motor nerve of the diaphragm). Prevention: 1. Children should get four doses of polio vaccine. One dose at each of the following ages: 2 months, 4 months, 6 – 18 months and 4 -6 years old. 2. Vaccine: - Inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV)- dead or inactive virus. - Oral poliovirus vaccine (OPV)- Weakened strain of live virus. Treatment: There is no cure for polio. 1. Supportive treatment (pain killer) can be provided for acute infection to reduce pain and bladder decompression. 2. Respiratory support for trouble breathing.

