

Nurse.ali fadel abassabout 4 years ago
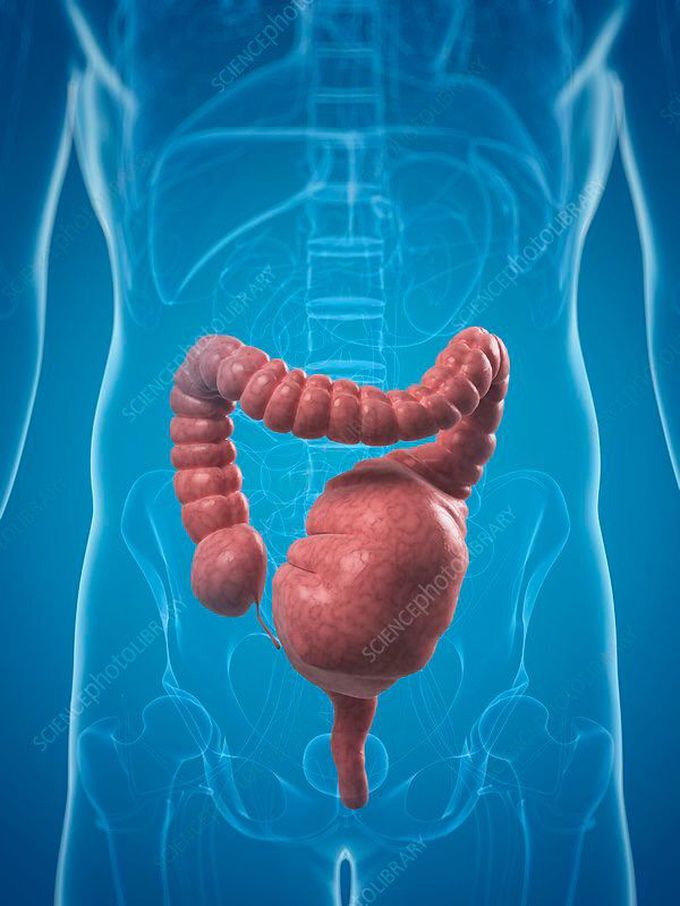
Toxic megacolon is a term used to express the seriousness of the condition. Toxic megacolon is rare. It’s a widening of the large intestine that develops within a few days and can be life-threatening. It can be a complication of inflammatory bowel disease (such as Crohn’s disease).When toxic megacolon occurs, the large intestines rapidly expand. Symptoms of the condition may come on suddenly and include: abdominal pain bloating of the abdomen (distention) abdominal tenderness fever rapid heart rate (tachycardia) shock bloody or profuse diarrhea painful bowel movements Toxic megacolon is a life-threatening condition. If these symptoms develop, you should seek immediate medical attention
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

