

Mishal Shanover 4 years ago
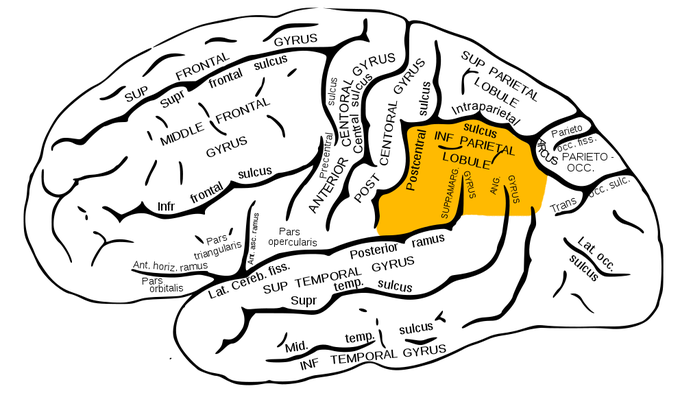
Gerstmann Syndrome
This refers to a constellation of findings arising as a result of a lesion at the angular gyrus near the junction of temporal and parietal lobes. Damage to this area compromises important functions of calculation, writing, counting fingers and left-right orientation. Patients, thus, present with alexia, agraphia, acalculia, finger agnosia, left-right disorientation. In adults, the most common etiology is a stroke.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!
Related posts
herniation secondary to raised ICPHyperekplexiaSymptoms of HyperekplexiaDandy Walker Malformation | Diagnosis symptoms and treatment2-Minute Neuroscience: Brain AneurysmsSeizures (Epilepsy) Nursing NCLEX: Tonic-Clonic, Generalized, Focal, SymptomsStroke: Causes, Risk Factors, Treatment, and Prevention | Mass General BrighamNeurofibromatosisAbsence seizuresSymptoms of absence seizures

