
SM
Syed Mohammad Hasanover 1 year ago
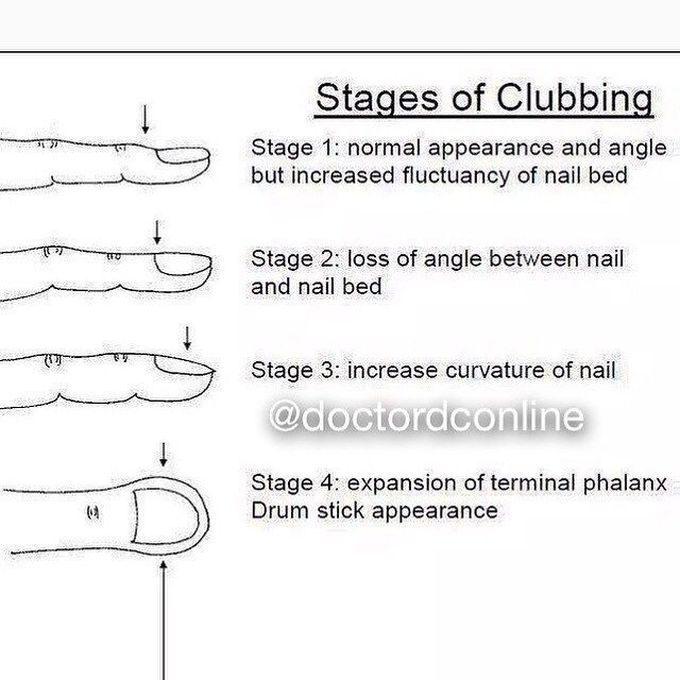
Stages of Clubbing
Nail clubbing refers to the nail changes that occur to to nail bed changes that lead to curvature or fluctuation changes in the nails. Clubbing is usually associated with conditions that lead to low blood oxygen levels such as some heart and lung diseases. Common causes include: - Congenital heart defects - Chronic lung infections - Interstitial lung disease (fibrotic) - Celiac disease - Cirrhosis of liver - Infective endocarditis and e.t.c The given image shows the stages of clubbing that is important to remember and keep in mind. Text Reference: https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/symptoms/clubbing-of-the-fingers-or-toes Image Source: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/437130707587558696/
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

