
Question
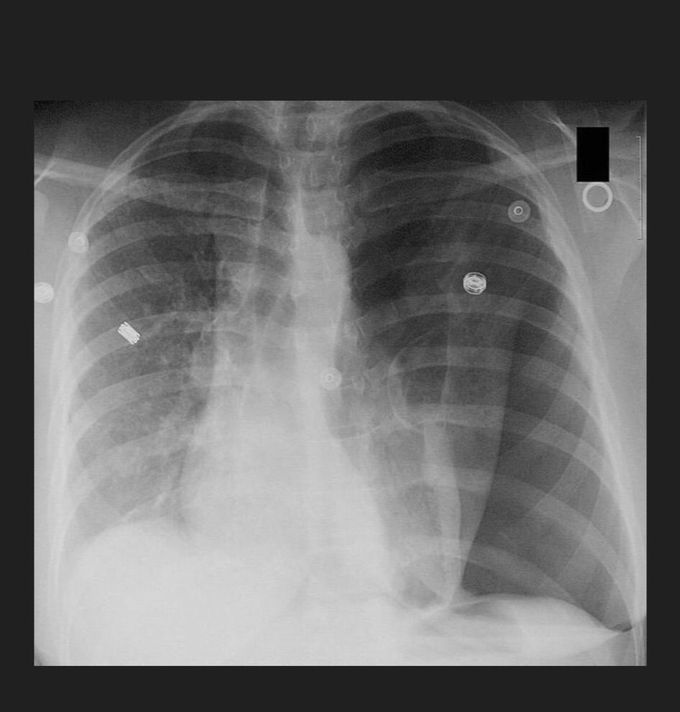
A 37-year-old male is brought to the emergency department following a motor vehicle accident. On arrival, respirations are shallow. Blood pressure is 80/60 mmHg, pulse is 122/min, and respiratory rate is 29/min. Physical examination demonstrates absent breath sounds on the patient's left side. Chest radiograph is shown. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management? A. Echocardiography B. Needle thoracostomy of the left second intercostal space C. Chest tube placement in the left fourth intercostal space D. Transfusion of packed red blood cells E. Endotracheal intubation
The correct answer is B. The patient's chest radiograph demonstrates a tension pneumothorax with collapsed lung. Needle thoracostomy in the left second intercostal space should be performed urgently. Tension pneumothorax is a medical emergency that occurs most frequently following trauma or lung infection. Physical exam findings include an absence of breath sounds on the side of the pneumothorax and hyperresonance to percussion in the ipsilateral lung. The injured lung acts like a one way valve such that air can enter the pleural space but cannot leave. Urgent needle thoracostomy is indicated to prevent cardiogenic shock and possible death. The Figure demonstrates a large left-sided tension pneumothorax. The mediastinum and trachea are shifted to the patient's right side. Answer C: Chest tube placement is indicated to prevent tension pneumothorax recurrence following needle thoracostomy.
C. Pneumothorax treatment. Remove the air and allow the lung to open up again and heal any damaged tissue. .
Latest guideline says.. Large bore needle in 5TH INTERCOSTAL SPACE ON ANTERIOR AXILLARY LINE.


