

Papillon–Lefèvre syndrome
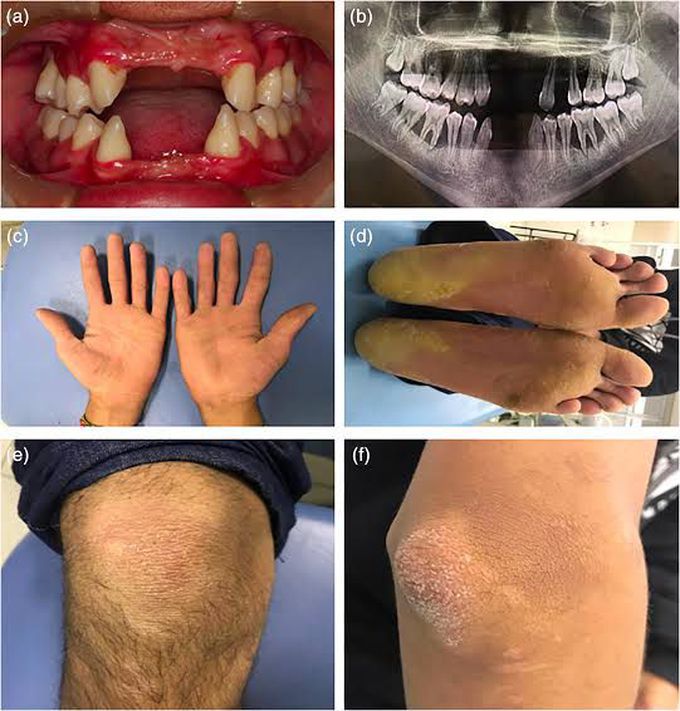
Papillon–Lefèvre syndrome (PLS) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder which occurs due to the mutation in 'cathepsin C gene' critical for appropriate immune response of myeloid and lymphoid cells, and important for normal structural growth and development of of skin. ORAL AND CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS : Clinically they present as Palmar plantar keratosis,hyperhidrosis, nail dystrophy, and keratosis on the elbows and knees. Dermatologically they present as yellow brown red flakes. Oral manifestations include dramatically advanced periodontitis seen in both deciduous and permanent dentition. At Age 4 to 5 all primary teeth have been lost or extracted. once edentulous the gingiva returns to normal health until the eruption of permanent dentition which then restarts the cycle. By age 15 all the permanent teeth have been lost. TREATMENT : The most successful treatment in this regard is systemic retinoids. Image by: https://images.app.goo.gl/8mygk2Le15VfZHo87
Retinoids are mainly helpful in treating dermatological manifestations

