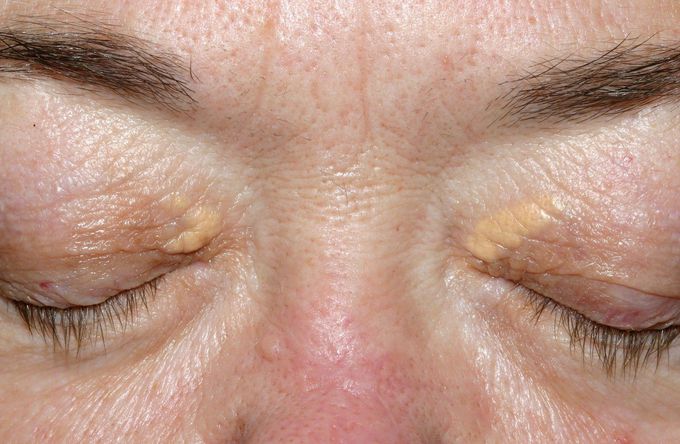
Medical Care Dietary restriction and pharmacologic reduction of serum lipids, although important in the overall care of a patient with abnormal lipids, yield only limited response in the treatment of xanthelasma.
Surgical Care Numerous options are available for the removal of xanthelasma palpebrarum, including surgical excision, argon and carbon dioxide laser ablation, chemical cauterization, electrodesiccation, and cryotherapy.
Chemical cauterization The use of chlorinated acetic acids has been found to be effective in the removal of xanthelasma. These agents precipitate and coagulate proteins and dissolve lipids. Monochloroacetic acid, dichloroacetic acid, and trichloroacetic acid have been used with good results. Haygood used less than 0.01 mL of 100% dichloroacetic acid with excellent results and minimal scarring. [5]