
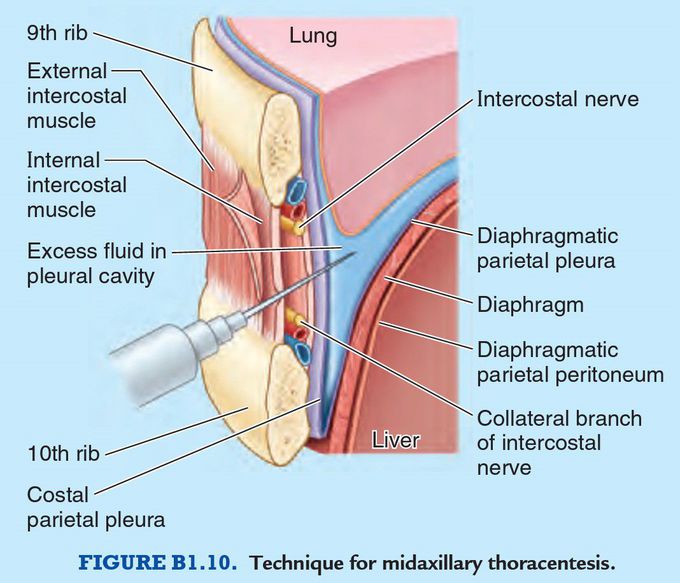
Thoracentesis
Sometimes it is necessary to insert a hypodermic needle through an intercostal space into the pleural cavity (thoracentesis) to obtain a sample of fl uid or to remove blood or pus . To avoid damage to the intercostal nerve and vessels, the needle is inserted superior to the rib, high enough to avoid the collateral branches. The needle passes through the intercostal muscles and costal parietal pleura into the pleural cavity. When the patient is in the upright position, intrapleural fl uid accumulates in the costodiaphragmatic recess. Inserting the needle into the 9th intercostal space in the midaxillary line during expiration will avoid the inferior border of the lung. The needle should be angled upward, to avoid penetrating the deep side of the recess (a thin layer of diaphragmatic parietal pleura and diaphragm overlying the liver).

