

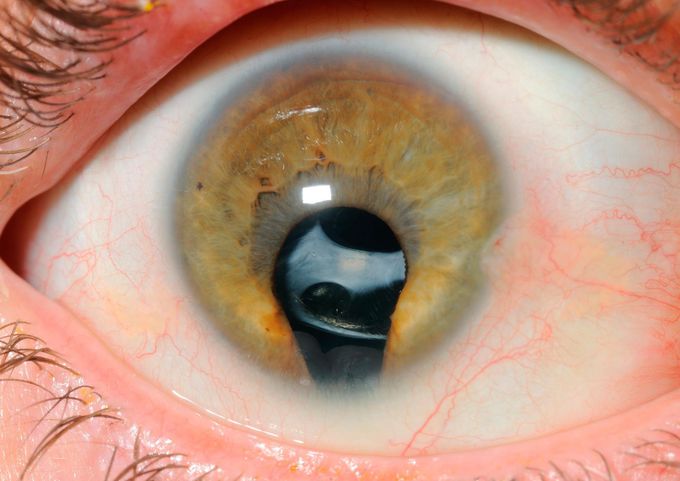
Coloboma of the Iris
Coloboma of the iris is a congenital defect caused due to improper closure of the embryonic fissure during the 5th week of gestation. Basically, a coloboma is a condition in which normal tissue of the eye is missing. In case of a coloboma of the iris, this leads to a typical "key-hole" or "cat-eye" appearance of the pupil. This eye abnormality may occur on its own or it may occur as a part of other chromosomal abnormalities. A coloboma of the iris generally does not affect the patient's vision. It may occur unilaterally or bilaterally and it's diagnosed clinically. Initially, the vision can be assessed by an ophthalmoscope and later visual acuity tests can be used once the child is old enough. There is no specific cure but affected individuals can wear colored contact lenses to make the iris appear rounded.

