

Fever of Unknown Origin (FUO) or Pyrexia of Unknown Origin (PUO)
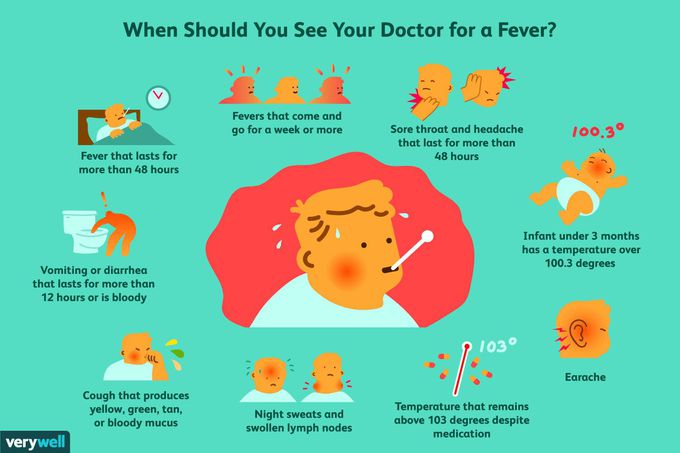
A temperature of >38.3 *C ( >100.9 *F) of at least 3 weeks' duration that remains undiagnosed following three outpatient visits or 3 days of hospitalisation. Presents with fever, headache, myalgia, and malaise. The differential diagnosis include: - Infectious: TB, endocarditis, osteomyelitis, sinusitis or CMV. - Neoplastic: lymphomas, leukaemias, hepatic and renal carcinoma. - Autoimmune: SLE, polyarteritis nodosa, sarcoidosis etc. - Miscellaneous: DVT, IBD, alcoholic hepatitis, factitious fever. - Idiopathic (10-15%) Diagnosis: Confirm the presence of fever and take detailed history including family l, sexual, occupational, exposure and travel history. Obtain a CBC, ESR, UA, blood and sputum culture, CXR, CT abdomen/pelvis. Specific test like ANA, RF, viral culture, antigen test can be done if infectious or autoimmune etiology is suspected. Treatment: Stop unnecessary medications. Patients with FUO and a completely negative work up have favorable prognosis, with fever resolving over months to years. Overall, infections and cancers account for majority of FUO cases (>60%). In elderly, rheumatic disease causes 1/3 of cases.

