

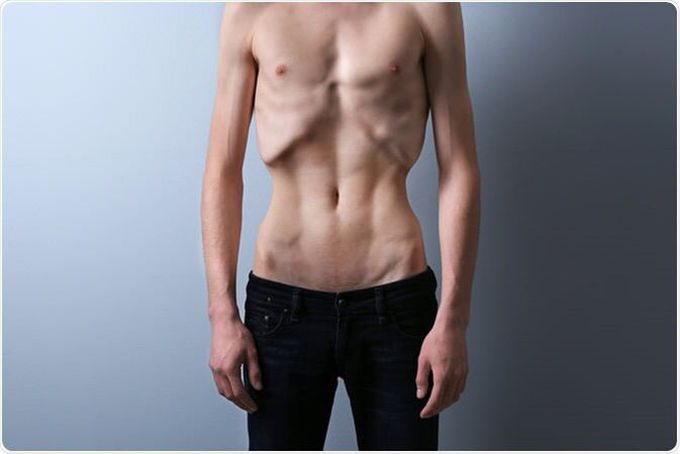
Anorexia Nervosa
More common in female gender. Risk factors include low self esteem and high socioeconomic status. Associated with OCD, mood disorders or anxiety. History: * Patients are often perfectionist and high achievers. * Divided into two subtypes 1. Restrictive: severe food restrictions. 2. Purging: severe eating compensated by purging (eg; excessive vomiting). Sign/Symptoms: * Cachexia * BMI less than 18.5 (kg/meter square) * Dry skin, bradycardia, lethargy, cold intolerance and hypothermia Diagnosis: * Measure height and weight. Check BMI; check CBC, electrolytes, endocrine levels and ECG. * Perform a psychiatric evaluation to screen patients for comorbid conditions. Treatment: * Monitor weight gain, hospitalize if necessary. * Watch for refeeding syndrome. * Psychotherapy; address maladaptive family dynamics. * Treat comorbidities. Anorexic patients are typically not distressed by their illness. They often deny health risks associated with their behaviour, making them resistant to treatment. Prolonged complications include seizures, osteoporosis, stress fractures, dental erosions and decay or even sudden death to name a few.
Wendigo syndrome

