

Lyme Disease
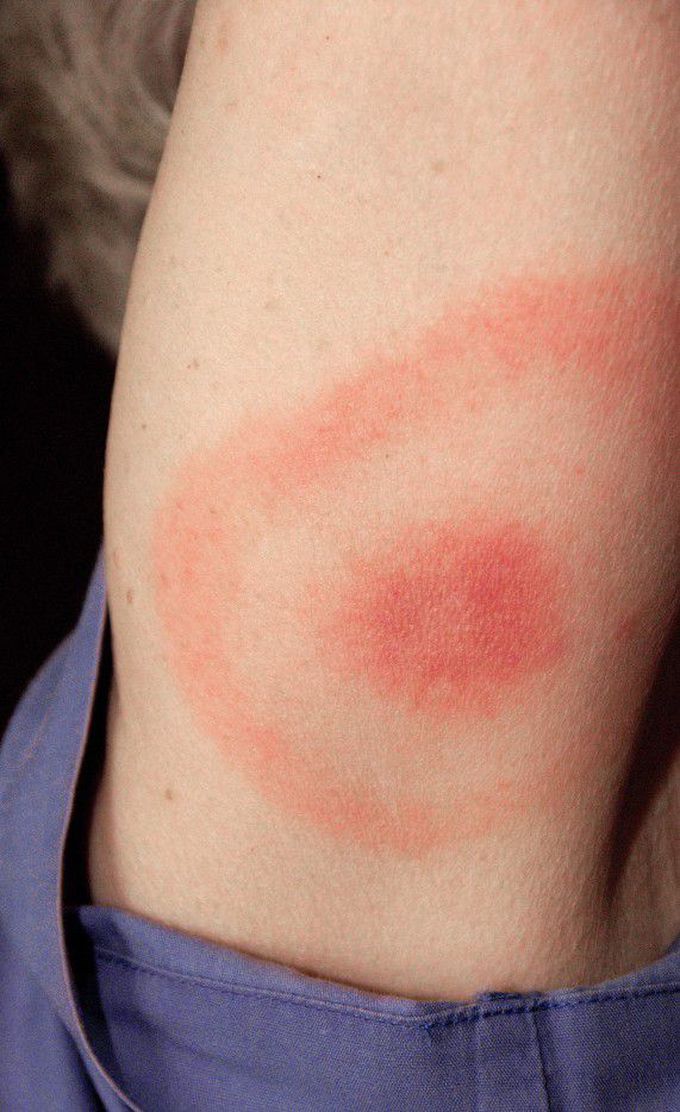
Lyme disease is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi which is transmitted to humans via the bite of infected ticks. The characteristic feature of this disease is a red "bull's eye" skin lesion at the bite site which is known as ERYTHEMA MIGRANS. However, erythema migrans is not pathognomonic of this disease. Along with this the patient can also have fever, headache, malaise, arthralgias and regional lymphadenopathy. Once dissemination occurs either through hematogenic or lymphatic routes, neurological involvement may occur like facial nerve palsy, lymphocytic meningitis etc. In advanced disease, patients may also have arthritis, encephalopathy and polyneuritis. Early diagnosis and proper antibiotic treatment of Lyme disease can help prevent late Lyme disease.

