

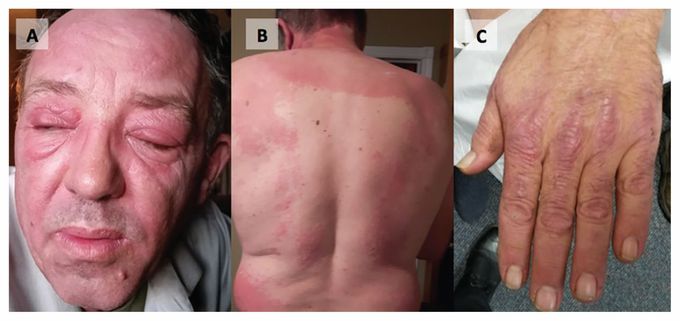
Dermatomyositis
It is an autoimmune, inflammatory disorder affecting the skin and skeletal muscle. It is characterized by bilateral, symmetric proximal muscle weakness due to which the patient has difficulty in performing certain physical activities like climbing stairs etc. The pathognomonic skin findings are violaceous, scaly patches symmetrically over knuckles, elbows and knees and these are called "Grotton's Papules". Other findings include heliotrope eyelids, shawl sign, dysphagia, fatigue and myocarditis. It's also associated with increased risk of malignancy especially in the ovaries. Diagnosis is made by performing a muscle biopsy along with measuring creatine kinase, aldolase, anti-neutrophilic antibodies and the anti-Jo-1 antibody. The standard treatment is a corticosteroid drug but immunosuppressant drugs, physical therapy and exercise are beneficial for treating it too.

