

Hiba Saleemover 4 years ago
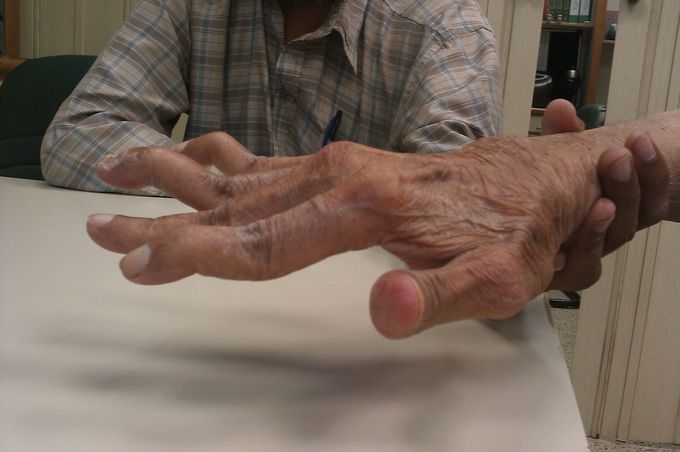
Swan Neck Deformity
Swan neck deformity of the finger is characterized by hyperextension of the proximal interphalangeal joint (PIP) and flexion of the distal interphalangeal joint (DIP). It occurs due to damage to the extensor mechanism of the finger. There are multiple causes such as injury to the extensor tendon by a traumatic laceration, weakening at the DIP from chronic inflammation or even due to extensor tendon subluxation as a result of an inflammatory disease most commonly rheumatoid arthritis.

