

Causes and Phases of Finger Clubbing
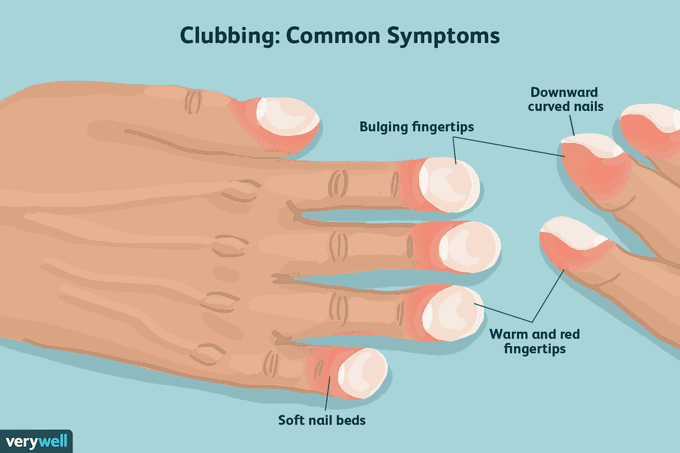
Clubbing of fingers is one of the common findings in general physical examination. Clubbing of fingers refers to progressive changes in the nails secondary to underlying disease causing widening of the nail, downward curling of the nail, increase in the angle between nail and cuticle, and softening of nail beds. The clubbing is usually progressive. It undergoes various phases. These are: Phase I: Increased fluctuation of the ungual bed Phase II: Loss of angle between nail and the cuticle (the normal value is 15 degrees). Phase III: Increase in the convexity of the nail bed. Phase IV: Drumstick appearance of the nail Phase V: Longitudinal striae on nails along with increased thickening of distal phalange The causes of the clubbing can be pulmonary or non-pulmonary. Common pulmonary causes of clubbing are: - Cystic fibrosis - Asbestosis - Lung cancer - Pulmonary fibrosis - Bronchiectasis Common non-pulmonary causes of finger clubbing are: - Hepatic disorders - Hodgkin’s lymphoma - Congenital cardiac anomalies such as tetralogy of Fallot - Grave’s disease - Crohn’s disease Reference: https://www.healthline.com/health/clubbing-of-the-fingers-or-toes#causes https://www.slideshare.net/khushyy/clubbing-54538042 Image courtesy: https://www.verywellhealth.com/clubbing-of-fingers-914776
Living with Pulmonary Fibrosis (PF) was one of the hardest experiences of my life. The breathlessness, the fatigue, and the fear of the future weighed on me every single day. I had tried so many treatments and medications, but nothing seemed to stop the disease from progressing.Out of both hope and desperation, I came across NaturePath Herbal Clinic. At first, I was skeptical but something about their natural approach and the stories I read gave me the courage to try one more time.I began their herbal treatment program, and within a few weeks, I noticed small changes easier breathing, more energy, and a clearer mind. Over themonths, those improvements became more and more obvious. Today, I can truly say my life has changed. My lungs feel stronger, and my quality of life has returned in ways I didn’t think were possible.This isn’t just a testimony it’s a heartfelt recommendation to anyone struggling with PF or other chronic conditions. Don’t give up hope. I’m so grateful I gave NaturePath Herbal Clinic a chance. Visit their website to learn more: www.naturepathherbalclinic.com info@naturepathherbalclinic.com


