

Ramsha Zaheerover 4 years ago
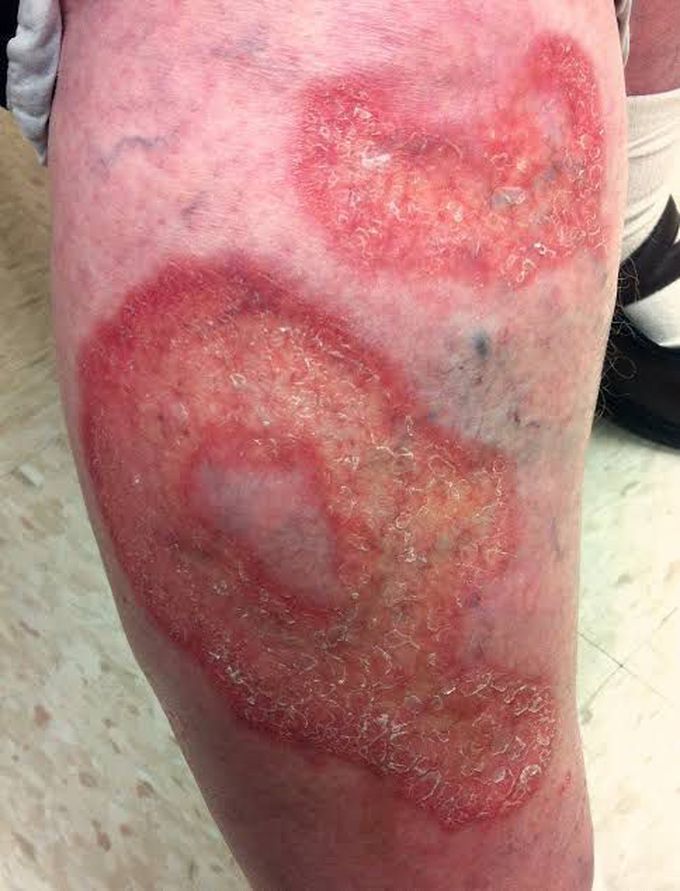
Necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum
Necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum is usually located over the anterior surfaces of the legs or the dorsal surfaces of the ankles. They are oval or irregularly shaped plaques with demarcated borders and a glistening yellow surface and occur in women two to four times more frequently than in men. Pathologically, the lesions show degeneration of collagen, granulomatous inflammation of subcutaneous tissues and blood vessels, capillary basement membrane thickening and obliteration of vessel lumina. The condition is associated with type 1 diabetes, although it can occur in patients with type 2 diabetes. First line therapy includes topical and subcutaneous corticosteroids. Improving glycemic control may help the condition.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!


