

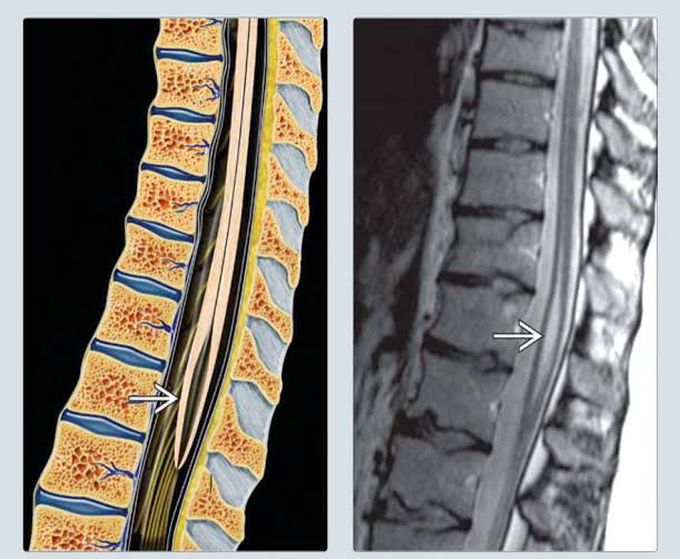
Terminal Ventricle or Ventriculus Terminalis
The terminal ventricle (ventriculus terminalis) - sometimes also known as 5th ventricle - is widest part of the central canal of the spinal cord, lined by ependyma, that is located at or near the conus medullaris. The central canal expands as a fusiform terminal ventricle, and is approximately 8–10 mm in length in the conus medullaris (or conus terminalis). Although the terminal ventricle is visible in the fetus and children, but is usually absent in adults. In some rare cases, it can persist in adults, where it can be an occasional finding on radiological investigations or it can display insidious and non-specific symptoms due to progressive cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) accumulation and cystic enlargement of the cavity. Symptoms may vary from aspecific signs to sphincter dysfunctions and focal neurological deficits. The correct management of this condition is still an object of debate due to its rarity and its unpredictable behaviour in adult patients. Only those patients with neurological deficits clearly related to the terminal ventricle could benefit from surgery.


