

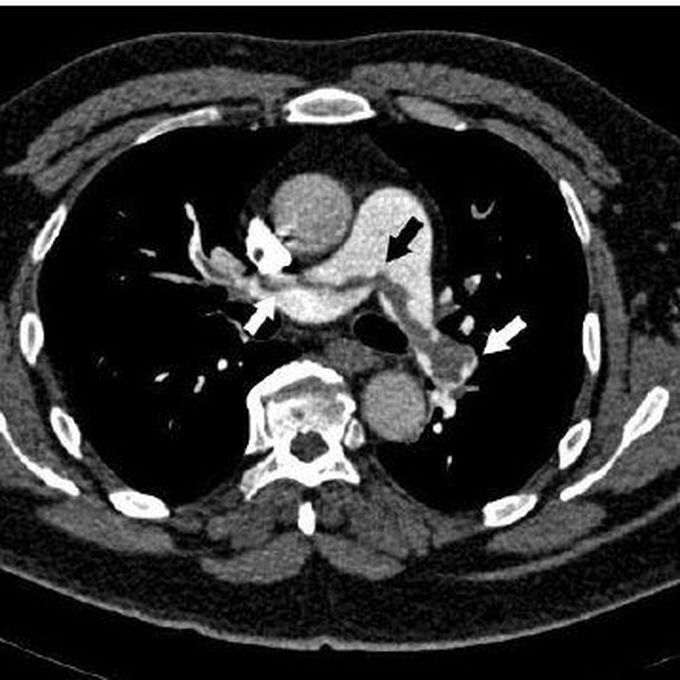
Pulmonary Embolism: Causes, Risk Factors, Signs and Symptoms, and Management
Pulmonary embolism is a potentially life-threatening condition, which occurs due to dislodging of deep vein thrombus/thrombi, resulting in blockage of pulmonary artery. Most common cause of pulmonary embolism is deep vein thrombosis. Pulmonary artery may also be blocked by fat embolism, air embolism, or a fragment of tumor. The symptoms usually depend on the size of the thrombus and the area of the lung involved as well as the comorbidities of the patient. Most common signs and symptoms are: - Shortness of breath: Sudden; worsens with exertion - Chest pain: Sharp pain associated with breathing; cough and bending over also worsen the pain - Cough: Associated with blood-streaked sputum - Irregular, rapid heartbeat - Loud S2 is heard on auscultation. S3 gallop may also be present. - Dizziness - Fever - Sweating - Cold, clammy and/or cyanotic skin Risk factors of pulmonary embolism are: - Family history of pulmonary embolism - Cardiovascular disorders e.g., heart failure - Malignancy: brain and ovarian tumors, CA pancreas, stomach cancer colon cancer, and malignancy of kidneys are associated with increased risk of blood clot formation - Surgery and bed rest: Prolonged immobilization increases risk of deep vein thrombosis and subsequent risk of embolism - Hypercoagulable states - Coivd-19: people with severe symptoms might develop pulmonary embolism - Smoking - Obesity - Pregnancy and estrogen supplements Diagnosis is based on detailed history, with emphasis on comorbidities, travel, and surgical history. Laboratory panel includes blood tests to look for elevated levels of D-dimers indicative of blood clots, hereditary conditions causing blood clots formation, and blood gases. The gold standard diagnostic modality for pulmonary embolism is pulmonary angiogram. Ultrasound, to look for deep vein thrombosis, and CT Chest with contrast is done to look for pulmonary embolism. Ventilation/perfusion scan may be done in case where contrast is contraindicated. MRI may be used for diagnosis in pregnant women where radiations should be avoided. The medical management of pulmonary embolism involves administration of anticoagulants and thrombolytics. Heparin is the most common used anticoagulant. Warfarin is also given orally as adjunct. Surgical options include insertion of vein filter to prevent passage of clot from legs to right side of heart or removal of clot if it is life-threatening and large in size via flexible catheter. Source Pulmonary embolism https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pulmonary-embolism/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20354653 Image via https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pulmonary_embolism

