

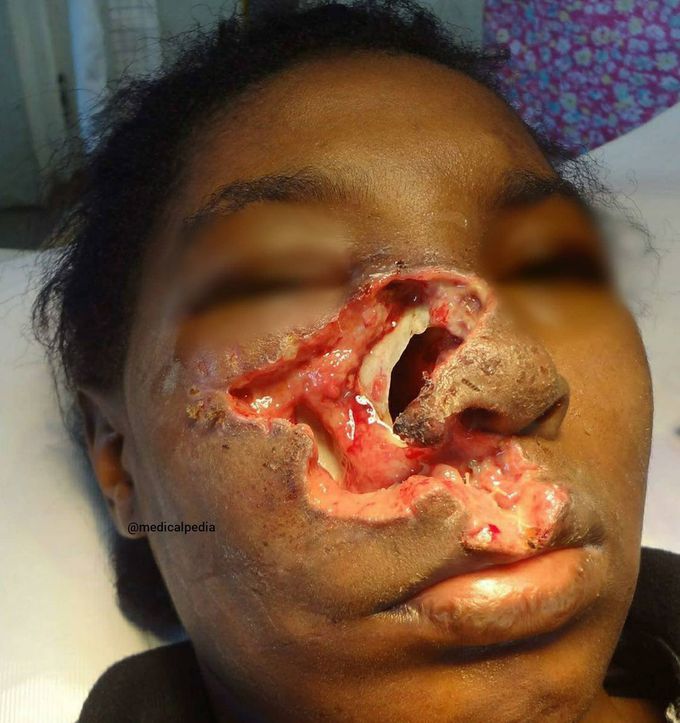
Rare case of mucormycosis- a fungal infection, affecting the right side of the patient's face!
Mucormycosis is a rare (0.43 to 1.7 cases per million per year) invasive fungal infection caused by various opportunistic fungi of the Mucoraceae family. Considered 100% fatal in 1960, previous the introduction of amphotericine, today the mortality ranges from 30-90% of all cases. A prompt diagnosis is the most critical aspect for an improved patient outcome. As swabs of tissue or discharge are generally unreliable, the diagnosis of mucormycosis tends to be established with a biopsy specimen of the involved tissue. Along with antifungal therapy, radical surgical debridement must be done expeditiously to eradicate this fungus.
Interestingly, this was my patient in 2012. She had maxillary swelling and foul breath. She had a CT that showed sinusitis. We performed a caldwell-Luc procedure and she improved. Interestingly, the wall of her maxillary sinus was already destroyed. She returned to the hospital 2 days later with dramatic facial and periorbital swelling. She also has an area of necrosis on the nose. I think this poor girl had rhinocerebral mucormycosis. This is a terrible disease with a 50% mortality .Pathology just showed inflammation. The patient expired. Today I read the following in Medscape "Earlier this year, hospitals in India were not only dealing with the coronavirus pandemic but also a surge in a potentially lethal fungal infection in patients previously treated for COVID-19. Mucormycosis, also known as black fungus, is typically a rare infection, but India had recorded over 45,000 cases as of July 2021.

