

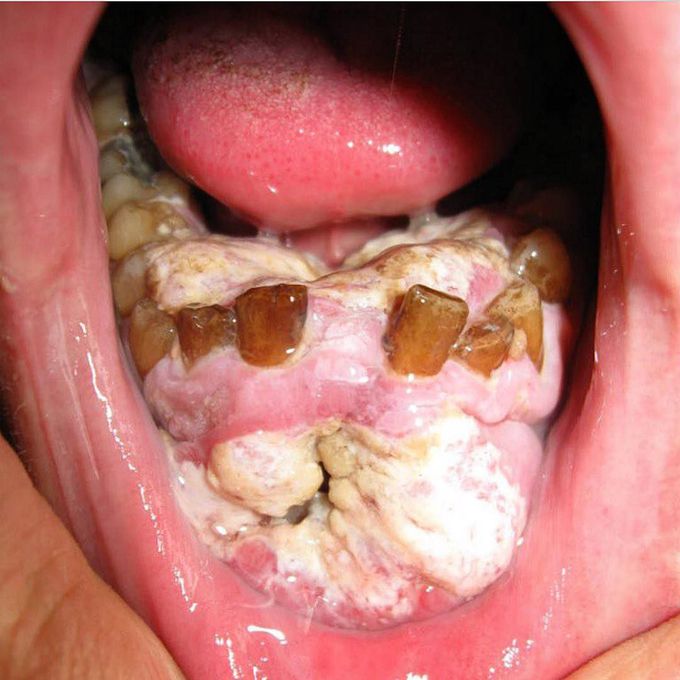
Advanced oral cancer in a 40 year old male smoker!!
This patient had history of leukoplakia, a precancerous condition of the mouth that lead to changes to cells of the mouth and make them more likely to develop into cancer. Leukoplakia is a condition of the mouth that involves the formation of white leathery spots on the mucous membranes of the tongue and inside of the mouth. It is not a specific disease entity and is diagnosed by exclusion of diseases that may cause similar white lesions like candidiasis or lichen planus. The cause in most cases is unknown, but many are related to tobacco use and chronic irritation. A small proportion of cases, particularly those involving the floor of the mouth or the undersurface of the tongue is associated with a risk of cancer. Oral squamous cell carcinoma in the most common intraoral site manifesting as a chronic, indurated ulcer. Tobacco is a potent risk factor for oral cancer. An interaction occurs between redox-active metals in saliva and the low reactive free radicals in cigarette smoke. The result is that saliva loses its antioxidant capacity and instead becomes a potent pro-oxidant milieu, as well as defective DNA repair which plays a significant role. Common physical examination findings of oral cancer include a lump or thickening in the oral soft tissues, soreness, difficulty chewing or swallowing or moving the jaw and tongue, hoarseness, numbness of the tongue or swelling of the jaw that causes dentures to fit poorly. The predominant therapy for oral cancer is surgical resection, radiation therapy, chemotherapy or a combination of all.
Mouth white lesion ddx. 1) keratotic ie scrape off, u due to candida 2)non keratotic ie can not scrape of either due to reactive hyperkeratosis as restorative tooth or leukoplakia (precancerous) or hairy leukoplakia which u bilateral and due to EBV or HIV and it is treatable

