

It's possible to reverse aging?!?
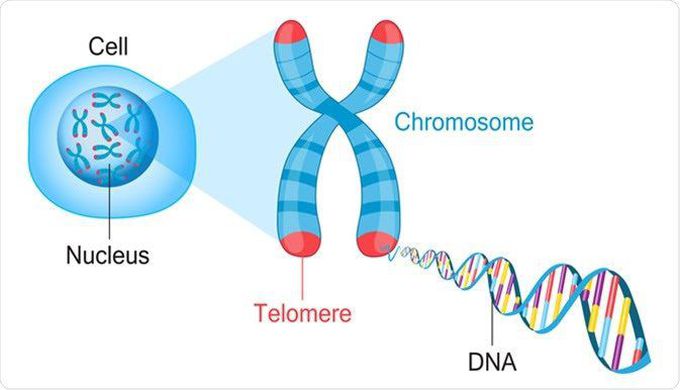
As Medical technology develops we keep trying to find ways to prolong the natural human lifespan. The current approach is to solve problems as they appear, but we can never fix them completely, only provide temporary relief since most of them are related to aging. Keeping that in mind, research into preventing the shortening of telomeres was started, although it did lead to some results, it was still not possible to fix the damage that had already been caused to the telomeres, not lengthen them. Telomeres are present at the end of chromosomes which prevent DNA from being lost during the replication of cells. Telomerase, an enzyme present in cells, repairs the damage to telomeres but not equal to the damage caused leading to subsequent shortening of the telomeres with each cell division. A cell with eventual shortening becomes a senescent cell which means it can no longer divide. Shortening of telomeres has been linked to several age-related diseases. New research suggests that it is possible to actually lengthen the telomeres. Lengthening of telomeres means that it is in theory possible to increase the lifespan of cells so that it takes longer until they reach the point of becoming a senescent cell. Researchers noticed that using hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), which utilizes 100% oxygen in an environmental pressure higher than one absolute atmospheres (ATA) to enhance the amount of oxygen dissolved in the body’s tissues, actually led to elderly patients becoming better. It was also noted that periodic treatments actually lead to the lengthening of telomeres in cells. Although this is a step in the right direction the expensive equipment involved, and the expertise required to operate, means that it will be very hard to bring to the public. References:- 1. Hachmo Y, Hadanny A, Abu Hamed R, Daniel-Kotovsky M, Catalogna M, Fishlev G, Lang E, Polak N, Doenyas K, Friedman M, Zemel Y, Bechor Y, Efrati S. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy increases telomere length and decreases immunosenescence in isolated blood cells : a prospective trial. Aging (Albany NY). 2020; . https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.202188 2. Image Credit: Fancy Tapis / Shutterstock

