

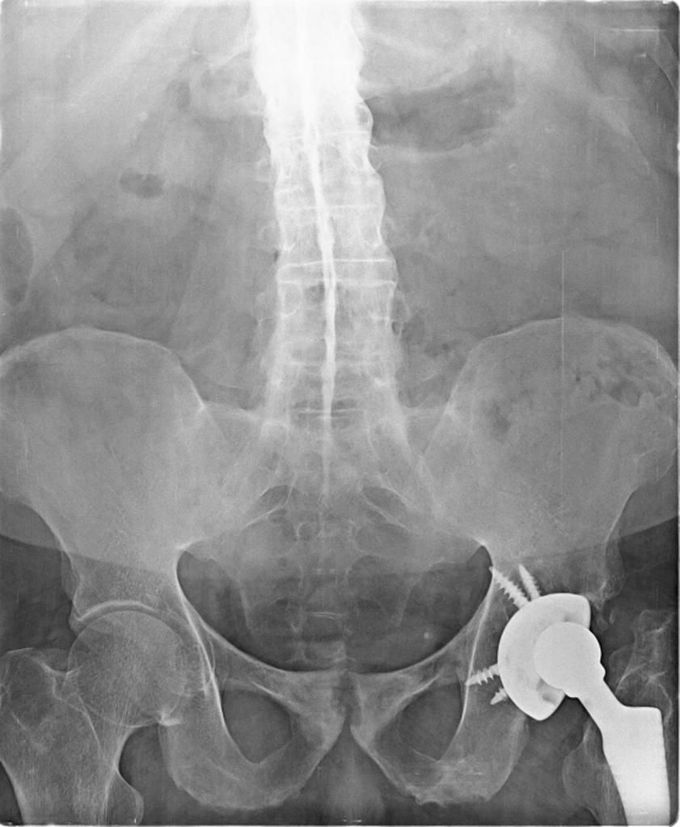
◼️Bamboo spine
🔸Bamboo spine is a radiographic feature seen in ankylosing spondylitis that occurs as a result of vertebral body fusion by marginal syndesmophytes. It is often accompanied by fusion of the posterior vertebral elements as well. 🔸 A bamboo spine typically involves the thoracolumbar and/or lumbosacral junctions and predisposes to unstable vertebral fractures and Andersson lesions. 🔸In a bamboo spine, the outer fibers of the annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral discs ossify, which results in the formation of marginal syndesmophytes between adjoining vertebral bodies. The resulting radiographic appearance, therefore, is that of thin, curved, radiopaque spicules that completely bridge adjoining vertebral bodies. 🔸There is also accompanying squaring of the anterior vertebral body margins with associated reactive sclerosis of the vertebral body margins (shiny corner sign). Together these give the impression of undulating continuous lateral spinal borders on AP spinal radiographs and resemble a bamboo stem; hence the term bamboo spine. 🔸Source: radiopedia

