

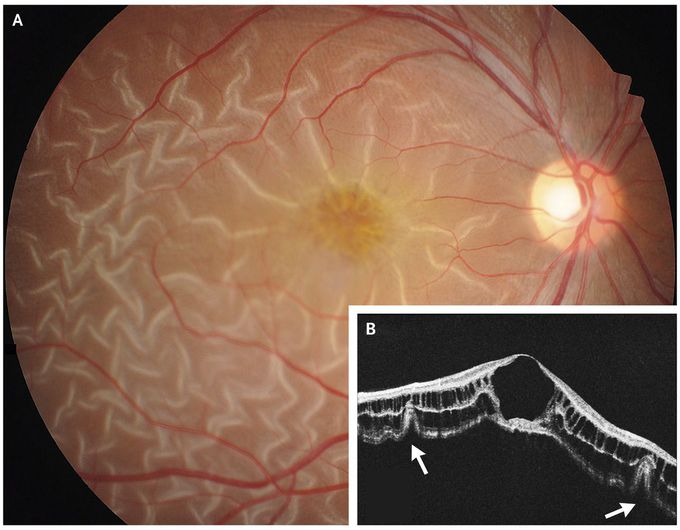
Retinal Detachment in X-Linked Retinoschisis
A 19-year-old man with X-linked retinoschisis presented with a 3-day history of worsening vision in his right eye. He had received a diagnosis of X-linked retinoschisis at 5 years of age, when reduced visual acuity and macular cystic degeneration were noted in both eyes. At the current visit, the visual acuity was 20/70 in the right eye and 20/40 in the left eye. Examination of the right fundus showed prominent retinal corrugations radiating from the fovea and normal vasculature (Panel A). Optical coherence tomography revealed a full-thickness retinal detachment and corrugation of deep layers of the retina (Panel B, arrows), as well as diffuse retinoschisis. X-linked retinoschisis is an inherited retinal disease that occurs primarily in males. Because no retinal tears were observed, the patient was treated nonsurgically. After a 2-week course of daily oral acetazolamide, the retinal detachment resolved. The patient’s visual acuity at follow-up had returned to a baseline of 20/40 in both eyes.

