
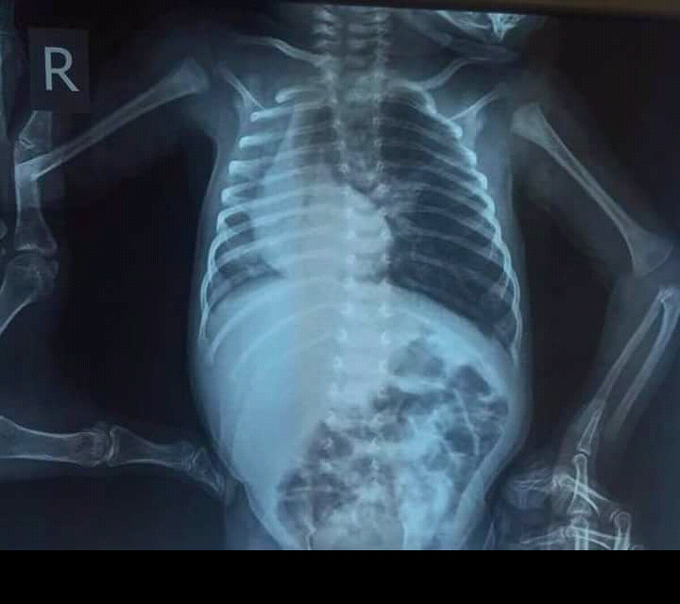
Dextrocardia (Right side heart)
Dextrocardia is a rare congenital condition in which the apex of the heart is located on the right side of the body.There are two main types of dextrocardia: dextrocardia of embryonic arrest and dextrocardia situs inversus. 1.Dextrocardia of embryonic arrest In this form of dextrocardia, the heart is simply placed further right in the thorax than is normal. It is commonly associated with severe defects of the heart and related abnormalities including pulmonary hypoplasia. 2.Dextrocardia situs inversus Dextrocardia with situs inversus refers to the heart being a mirror image situated on the right side. For all visceral organs to be mirrored, the correct term is dextrocardia situs inversus totalis. Although statistically people with dextrocardia do not have any medical problems from the disorder, they may be prone to a number of bowel, esophageal, bronchial and cardiovascular disorders (such as double outlet right ventricle, endocardial cushion defect and pulmonary stenosis).Certain cardiovascular and pulmonary disorders related to dextrocardia can be life-threatening if left unchecked. Kartagener syndrome may also be present in patients with dextrocardia but this must be in the setting of situs inversus and may include male infertility.
Triad of kartageners syndrome is situs inversus bronchiectasis and sinusitis


