
Testicular
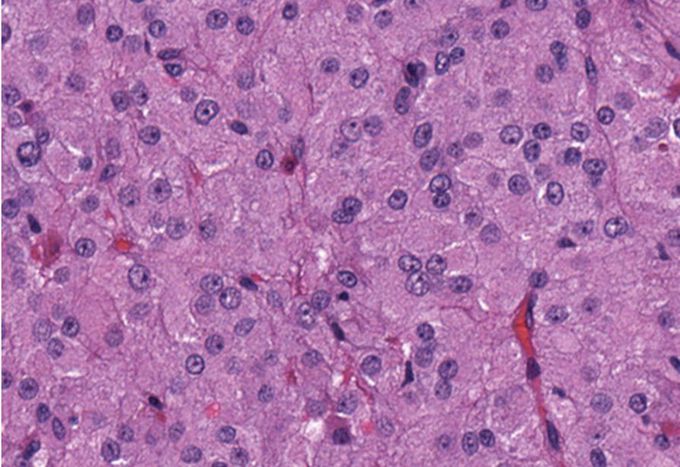
A 37-year-old man has noticed bilateral breast enlargement over the past 6 months. On physical examination, both breasts are enlarged without masses. His right testis is firm and 1.5 times larger than his left testis. His serum estrogen is increased. An ultrasound scan shows a circumscribed 2-cm mass in the body of the right testis. A right orchiectomy is performed, and grossly the mass has a uniform, brown cut surface. The microscopic appearance is shown in the figure. With electron microscopy the cells have rod-shaped crystalloids of Reinke. What is the most likely diagnosis? A. Choriocarcinoma B. Embryonal carcinoma C. Gonadoblastoma D. Leydig cell tumor E. Seminoma F. Teratoma G. Yolk sac tumor . The majority of Leydig cell tumors are found in males, usually at 5–10 years of age or in middle adulthood (30–60 years). Children typically present with precocious puberty. Due to excess testosterone secreted by the tumour, one-third of female patients present with a recent history of progressive masculinization. Masculinization is preceded by anovulation, oligomenorrhea, amenorrhea and defeminization. Additional signs include acne and hirsutism, voice deepening, clitoromegaly, temporal hair recession, and an increase in musculature. Serum testosterone level is high Leydig cell tumors of the testis are most often small, benign masses that may go unnoticed. Some patients have gynecomastia caused by androgenic or estrogenic hormone production (or both) by the tumor. Most patients are young to middle-aged men; sexual precocity may occur in the few boys who have such tumors. Choriocarcinomas are grossly soft and hemorrhagic masses that have large bizarre syncytiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast cells and are aggressive. Embryonal carcinomas are large, aggressive tumors that have a variegated gross appearance and primitive cells with large, hyperchromatic nuclei. Gonadoblastomas are rare testicular tumors that arise in the setting of gonadal dysgenesis. A pure seminoma can be uniformly brown on cut surface, but often has a lymphoid stroma, and is not likely to secrete androgens or estrogens. Pure teratomas are rare and contain elements of three germ layers. Yolk sac tumors have cells that organize into primitive endodermal sinuses (Schiller-Duval bodies).

