
Female reproductive disorder
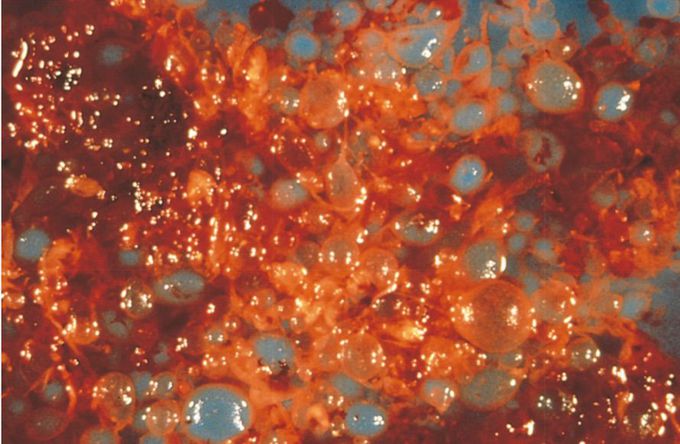
A 21-year-old G2, P1 woman is in the early second trimester. She has noted a small amount of vaginal bleeding for the past week and has had marked nausea and vomiting for 3 weeks. On physical examination, the uterus measures large for dates. An ultrasound examination shows intrauterine contents with a “snowstorm appearance,” and no fetus is identified. The gross appearance of tissue obtained by dilation and curettage is shown in the figure. Which of the following substances is most likely to be greatly increased in her serum? A. Acetylcholinesterase B. α-Fetoprotein C. Estradiol D. Human chorionic gonadotropin E. Human placental lactogen . . #usmle #usmlestep1 #mole The figure shows a hydatidiform mole, or complete mole, with enlarged, grapelike villi that form the tumor mass in the endometrial cavity. These trophoblastic tumors secrete large amounts of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). Molar pregnancies result from abnormal fertilization, with only paternal chromosomes present. Neural tube defects can be distinguished from other fetal defects (e.g., abdominal wall defects) by use of the acetylcholinesterase test on amniotic fluid obtained by amniocentesis.
D. It must be monitored for at least a year after the D&E. There us a correlation of her developing cancer.
Doc how does it differ from choriocarcinoma morphologically
Hcg, because , snowstorms appearance was find on hidrotiform mola



