
MRI Technologistabout 9 years ago
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
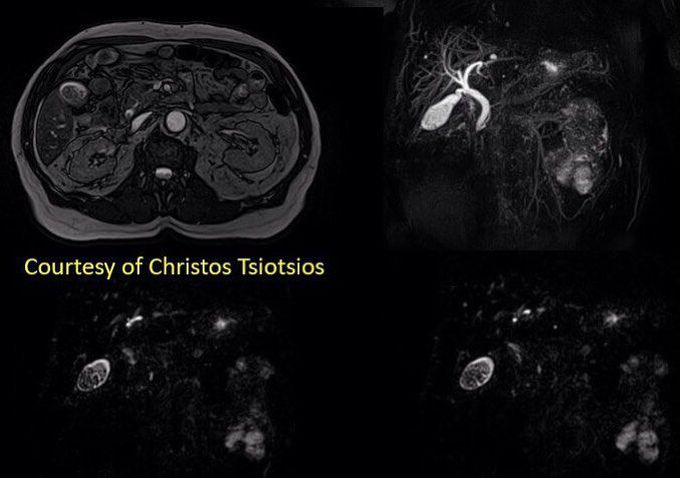
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is an MRI technique that is used to visualize the biliary and pancreatic ducts in a non-invasive manner. MRCP makes use of heavily T2-weighted MRI pulse sequences. These sequences show high signal in static or slow moving fluids within the gallbladder, biliary ducts and pancreatic duct, with low signal of surrounding tissue. Regarding its history, MRCP was introduced in 1991. Figure shows multiple gallstones and biliary tree dilatation. Gallstones are better highlighted on balanced SSFP (upper left) and native images of the 3D acquisition (bottom row), while biliary tree dilatation is better highlighted on MIP image of the 3D acquisition (upper right). Images courtesy Christos Tsiotsios.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

