
MRI Technologistabout 9 years ago
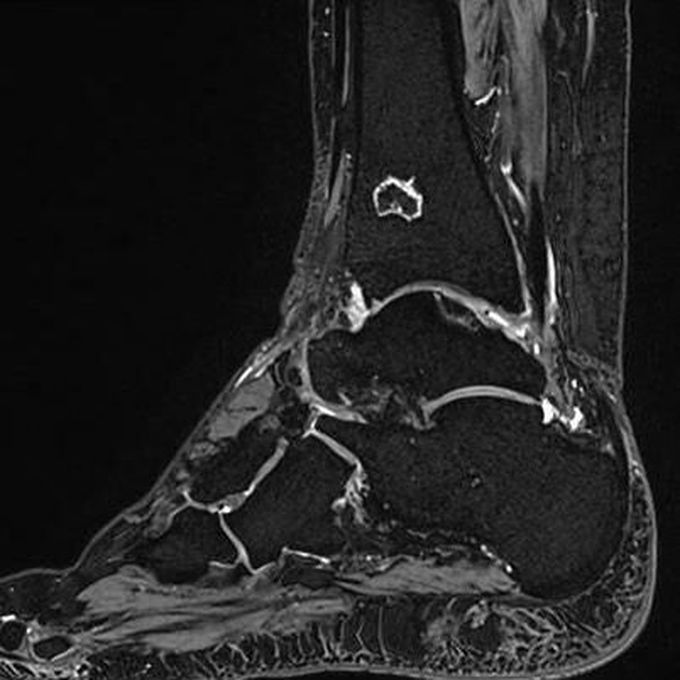
Water excitation technique is based on the chemical shift
A binomial (or composite) excitation pulse is used, which achieves minimum excitation of fat protons and maximum excitation of water protons. Thus, the fat protons will not contribute to the MR signal. Fig. Sagittal three-dimensional double-echo steady-state (3D DESS) MR image of the ankle with Water Excitation (WE). Water excitation technique provides high SNR and resolution with robust fat suppression within reasonable acquisition times. This technique is mainly used for cartilage imaging. Image dataset acquired at 3.0 Tesla. Image courtesy of Bac Nguyen.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

