
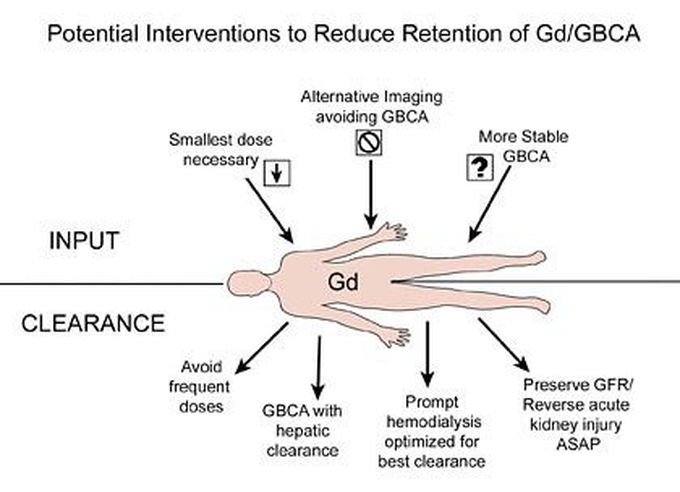
NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS (NSF)
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of GBCAs in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs. • The risk of NSF appears highest among patients with: – Chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR <30 mL/min/1.73m2), or – Acute kidney injury • Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (for example, age >60 years, hypertension or diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing. • For patients at highest risk for NSF, do not exceed the recommended Gd dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug from the body prior to any re-administration. Figure shows potential interventions to reduce the retention of Gd/GBCA can be divided into approaches that reduce input and increase clearance (figure from Kuo et al., 2009).

