
Liver disease
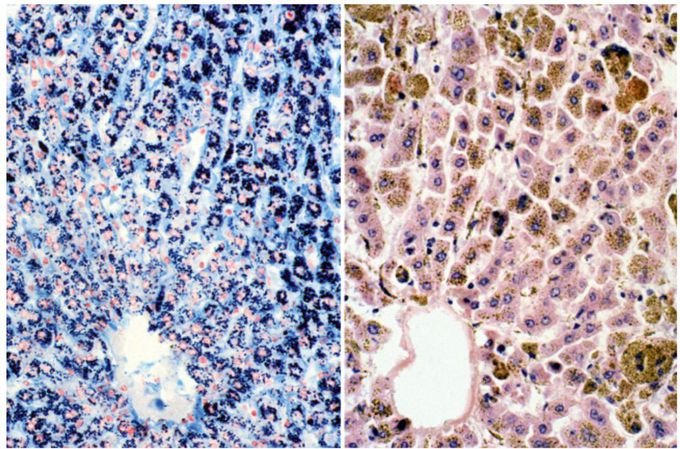
A 44-year-old man has had increasing arthritis pain, swelling of the feet, and reduced exercise tolerance over the past 3 years. Laboratory studies include serum glucose of 201 mg/dL, creatinine of 1.1 mg/dL, and ferritin of 893 ng/mL. A chest radiograph shows bilateral pleural effusions, pulmonary edema, and cardiomegaly. He undergoes a liver biopsy; the microscopic appearance of a biopsy specimen stained with H&E (right panel) and Prussian blue (left panel) is shown in the figure. Based on these findings, which of the following is the most appropriate therapy for this patient? A. Cholecystectomy B. Interferon-α C. Phlebotomy D. Prednisone E. Reduce alcohol intake
Answer: C. This Patient has Hereditary hemochromatosis (HHC) Pathogenesis 1. Unrestricted reabsorption of iron in the small intestine 2. Mutations involving hereditary hemochromatosis gene (HFE), C282Y & H63D on chromosome 6 Clinical findings: 1). Cirrhosis, 2). Bronze diabetes, 3). Malabsorption, 4). Restrictive cardiomyopathy, 5). Hypogonadism,6). Degenerative joint disease Treatment: 1). 🔺Phlebotomy until ferritin < 50 ug/ml, 2). Deferoxamine


