

Beccaalmost 8 years ago
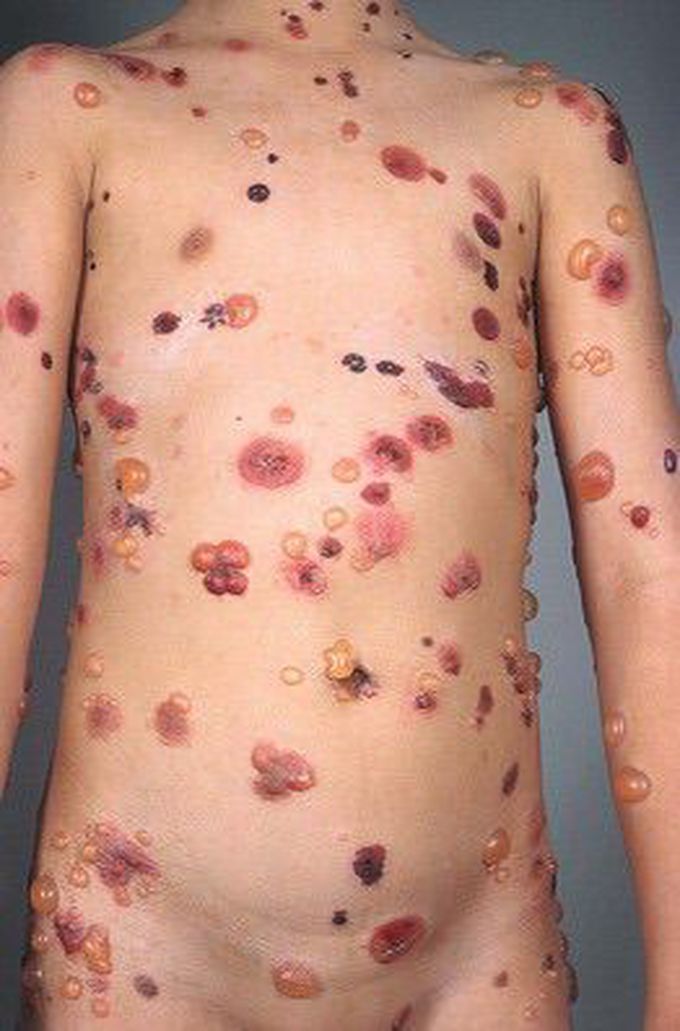
Bullous Pemphigoid
Bullous Pemphigoid is a rare, subepidermal blistering disease. Direct immunoflorescence studies on Bullous Pemphigoid patients reveal linear bands of immunoglobulin G (IgG) separating the dermis and epidermis. Therefore, the blisters are caused by an autoimmune response, which can be spontaneous or due to taking certain medications. Treatment usually includes immunosuppressants or anti-inflammatory agents like corticosteroids and dapsone.
Other commentsSign in to post comments. You don't have an account? Sign up now!

