

Oral HPV-Associated Papillomatosis in AIDS
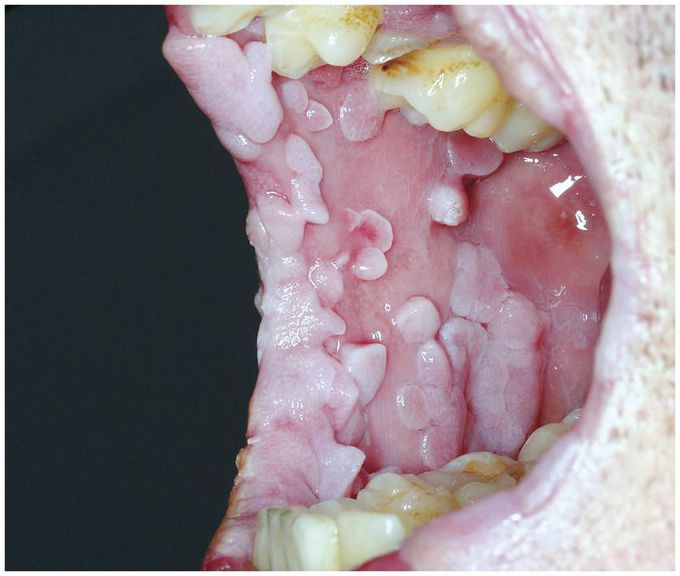
A 36-year-old man who had the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) with Kaposi’s sarcoma was referred for evaluation of a 2-year history of extensive, painless oral papillomatous lesions (viewed here from the patient’s left side). His sexual history included sex with men, and his partner had a history of anogenital warts. The patient was receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy. The blood level of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 was under 20 copies per milliliter, and the CD4+ T-cell count was 318 per milliliter. The physical examination revealed widespread labial, palatal, and oral nodular warty lesions consistent with condyloma acuminatum. Histopathological and immunohistochemical studies confirmed the diagnosis and detected human papillomavirus (HPV) types 6 and 11. During the subsequent 2 years, the patient underwent multiple sessions of carbon dioxide laser therapy to remove the oral lesions. HPV-associated warty lesions in patients who are coinfected with HIV can be more persistent, extensive, and aggressive than those in patients without HIV infection. Impaired immune surveillance (a CD4+ T-cell count of <200 cells per milliliter) may reduce the effectiveness of conventional therapy for HPV and increase the risk of condyloma recurrences.
Living with HIV was one of the hardest experiences of my life. The fatigue, the emotional toll, and the uncertainty about the future weighed on me every single day. I had tried many treatments and medications, but nothing seemed to restore my health or energy the way I hoped.Out of both hope and desperation, I came across NaturePath Herbal Clinic. At first, I was skeptical but something about their natural approach and the powerful stories I read gave me the courage to try one more time.I began their herbal treatment program, and within a few weeks, I noticed small but meaningful changes more energy, better sleep, and a stronger immune system. Over the months, those improvements only grew. Today, I can truly say my life has changed. I feel healthier, more balanced, and finally in control of my well-being again.This isn’t just a testimony it’s a heartfelt recommendation to anyone living with HIV or any chronic condition. Don’t give up hope. I’m so grateful I gave NaturePath Herbal Clinic a chance. Visit their website to learn more: www.naturepathherbalclinic.com Email: info@naturepathherbalclinic.com


