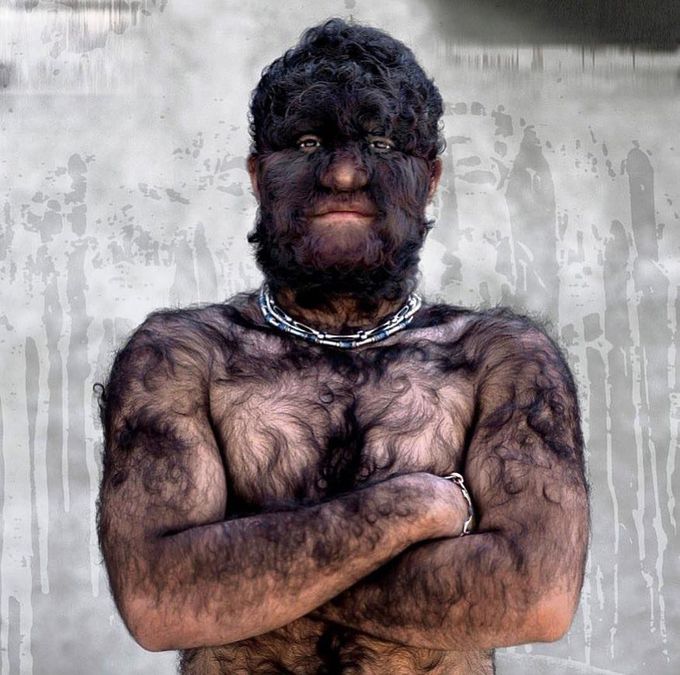


Hypertrichosis
The excessive hair growth above the normal for the age,sex and race of an individual. When hypertrichosis is hormonal in origin, then it is termed as Hirsuitism. Hypertrichosis may be congenital or acquired. •Cause: The cause of hypertrichosis is unknown. Congenital hypertrichosis is believed to be a genetic disorder that is inherited or occurs as a result of spontaneous genetic mutation. •Treatment: Treatment of hypertrichosis is hair removal. Several methods are available but need to be repeated regularly as hair continues to grow back and are: - Repeated shaving. - Chemical epilation. - Electrolysis and thermolysis. - Waxing. More recently, laser hair removal has been proposed as a treatment option for hypertrichosis. The man above has a very rare type of hypertrichosis called "Congenital Hypertrichosis Lanuginosa". Only about 50 cases of this type has been reported worldwide.
Acquired Hypertrichosis Lanuginosa
🍄 Commonly noticed Triads; Pentads🍚🍚 1. Hutchinson's Triad (congenital syphilis): - Hutchinson's teeth (notched incisors) - Interstitial keratitis - Deafness due to involvement of the eighth cranial nerve 2. Charcot's Triad(for cholangitis): - Jaundice - Fever with chills - Right upper quadrant pain 3. Samter's triad -bronchial asthma -nasal polyps - aspirin intolerance 4. Triad of O'Donoghue (or unhappy triad, often seen in sports injuries, especially knee injuries): - ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) tear - MCL (medial collateral ligament) tear - Medial meniscus tear 5. Beck's Triad (cardiac tamponade): - Distant/muffled heart sounds - Increased jugular venous pressure - Hypotension 6. Saint's Triad: - Gallstones - Diverticulosis - Hiatal hernia 7. Whipple's Triad: - Symptoms of hypoglycemia - Documented low blood sugar - Relief of symptoms after glucose administration 8. Cushing's Triad (seen in increased intracranial pressure): - Hypertension - Bradycardia - Irregular or abnormal respirations 9. Virchow's Triad(risk factors for thrombosis): - Endothelial injury - Stasis or turbulent blood flow - Blood hypercoagulability 10. Triad of Alport Syndrome: - Hematuria - Sensorineural hearing loss - Ocular abnormalities 11. Reynold's Pentad (an extension of Charcot's Triad for advanced cholangitis): - Jaundice - Fever with chills - Right upper quadrant pain - Septic shock - Mental confusion

